Figure 1.
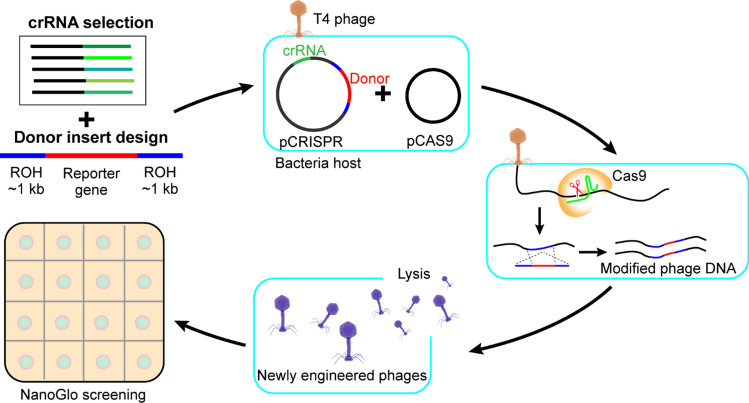
CRISPR/Cas9 T4 Phage Engineering Workflow. Candidate crRNAs targeting the T4 gene of interest were validated by a plaque assay. The most effective crRNA was selected based on largest reduction in Efficiency of Plating (EOP) and inserted into the synthetic CRISPR array in pCRISPR. The donor insert was designed to contain a reporter gene flanked by regions of homology to the crRNA recognition sequence and cloned into pCRISPR. A strain containing pCas9 and pCRISPR was infected with T4 phages. CRISPR/Cas9-mediated T4 genome cleavage followed by homologous recombination with the donor plasmid resulted in genomic incorporation of the reporter gene. NanoGlo screening was used for luminescent detection of recombinant phages by addition of the reporter enzyme substrate to phage plaques.