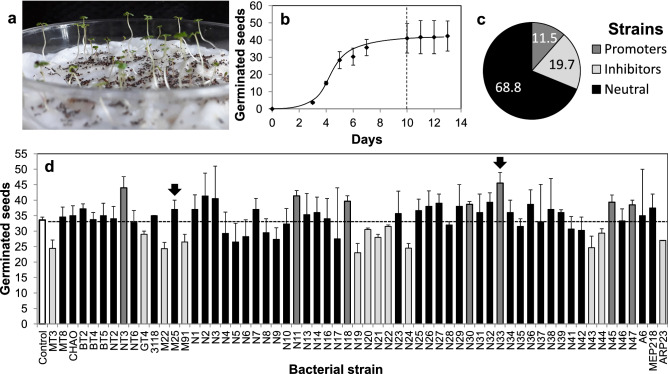
Figure 1.
Selection of bacterial strains for their effect on germination. In all cases, we counted the number of germinated E. grandis seeds from 50 mg of commercial seed mixture. (a) Germination plate ten days after imbibition. (b) Germination rate of uninoculated E. grandis seeds. The dotted line indicates the tenth day, when the maximum germination is reached. Data shown are the means, n = 3, error bars represent SEM. (c) Proportion of tested bacterial strains resulting in promotion, inhibition or no effect on E. grandis seed germination. (d) Number of emerged seedlings on the tenth day after inoculating seeds with axenic suspensions of different bacterial strains (1 × 108 CFU ml−1) or with distilled water (control, white bar). Data shown are the means, the dotted horizontal line indicates the mean of the control treatment. n = 3, error bars represent SEM. Light gray, dark gray and black bars show bacterial strains with negative, positive or no effect on germination, respectively (CI = 95%). Strains M25 and N33 (indicated with arrows) were selected for further studies.