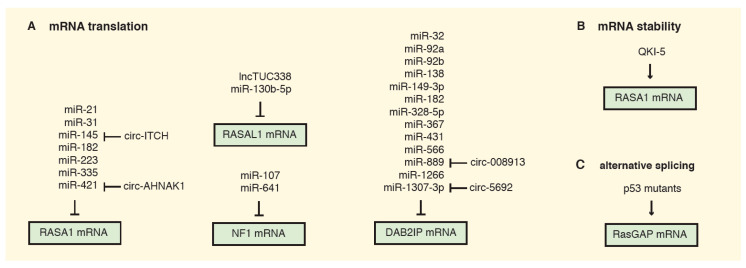
Figure 2.
Schematic overview of current evidence for post-transcriptional regulation of RasGAPs. (A) MicroRNA-dependent regulation. Both miRNAs and long non-coding RNAs (lncRNA and circ-RNA) are involved in modulating RasGAP mRNA translation both directly and indirectly. (B) Control of mRNA stability. Stability of RASA1 mRNA can be fostered by direct binding with the RNA-binding protein Quaking-5 (QKI-5); loss of QKI-5 can reduce RASA1 expression in cancer. (C) Control of alternative splicing. Expression of missense p53 mutant proteins enhances the inclusion of cytosine-rich exons in the mRNA of RasGAPs; the encoded proteins show defects in membrane association and reduced Ras inhibitory function.