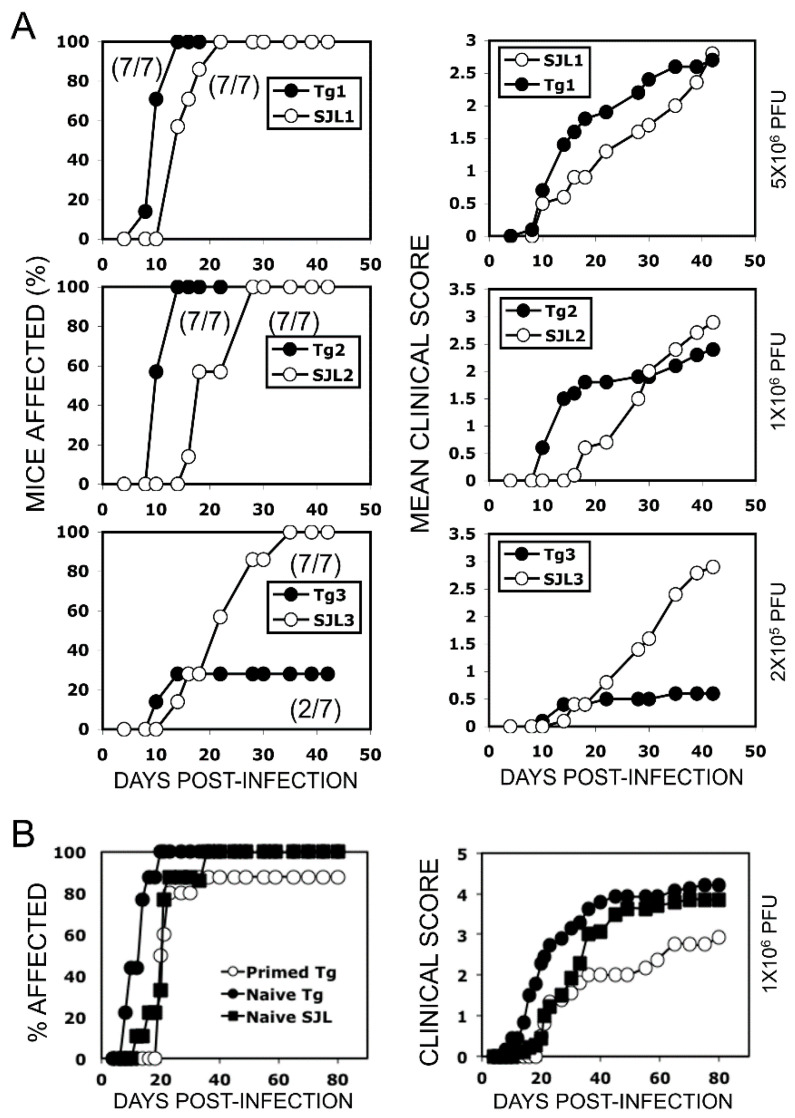
Figure 3.
Effects of virus infection-dose and virus-reactive CD4+ T cells on the development of demyelinating disease. (A) Different viral doses (2 × 105, 1 × 106 and 5 × 106 PFU) were used to infect SJL mice receiving VP2-TCR-Tg or control SJL CD4+ T cells to compare the development of clinical symptoms for 45 days. CD4+ T cells were purified using a negative selection column. Purified CD4+ T cells (1 × 106/mouse) were injected through the tail-base vein of naive SJL mice. Recipient SJL mice (n = 7) were infected intra-cerebrally with the indicated PFUs; 5 × 106 PFU (upper row), 1 × 106 PFU (middle row), and 2 × 105 PFU (bottom row). Clinical signs were scored two times per week for 50 days. The mean disease score (left column) and % of affected mice (right column) are shown. The two-tailed p values between the groups were significant based on the paired t test of the mean clinical cores, with p < 0.0001 (t = 17.080 with 7 degrees of freedom) in the upper row groups between days 10 and 35, p = 0.0219 (t = 2.309 with 6 degrees of freedom) in the middle row groups between days 10 and 30, and p = 0.0065 (t = 4.428 with 5 degrees of freedom) in the bottom groups between days 20 and 42. (B) Purified CD4+ T cells (2 × 106 cells/mouse) stimulated in vitro with PBS or VP274-86 for 6 h were transferred into naive SJL mice and then infected with TMEV (1 × 106 pfu/mouse). The developments of clinical symptoms were compared among these experimental groups (n = 10) over 80 days postinfection. The two-tailed p values between the groups were significant based on a paired t test of the mean clinical cores between days 8 and 40 postinfection: p < 0.0001 (t = 8.534 with 13 degrees of freedom) between the group receiving naive VP2-TCR-Tg CD4+ T cells and the group receiving VP2-primed VP2-TCR-Tg CD4+ T cells, p < 0.0159 (t = 2.771 with 13 degrees of freedom) between the group with VP2-primed Tg CD4+ T cells and the group with naive SJL CD4+ T cells, and p < 0.0001 (t = 7.389 with 13 degrees of freedom) between the group with naive VP2-TCR-Tg CD4+ T cells and the group with naive SJL CD4+ T cells.