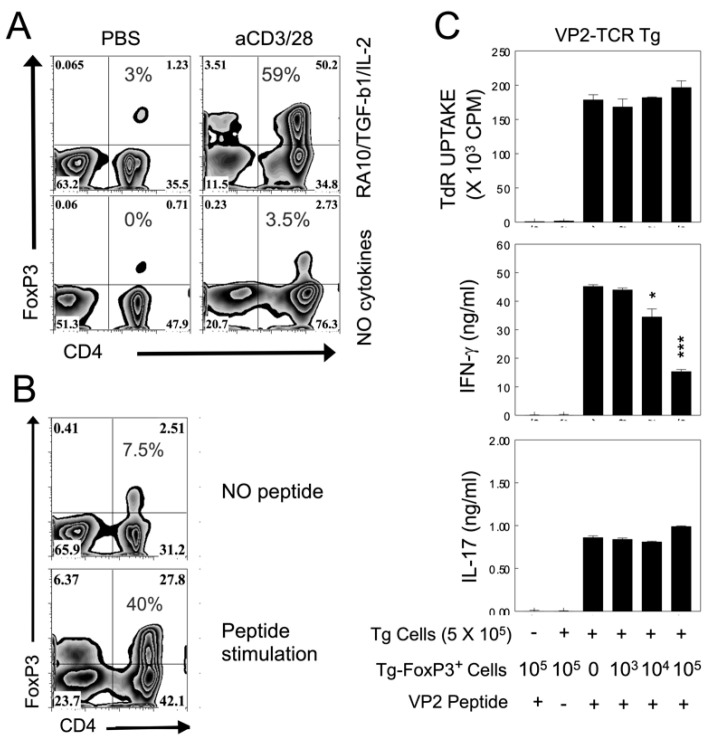
Figure 6.
Role of VP272-86 specific FoxP3+CD4+ T cells in the regulation of T cell cytokine production. (A) In vitro generation of FoxP3+CD4+ T cells in the presence or absence of T cell stimulants and/or added cytokines (10 nM retinoic acid, TGF-β, IL-2). Purified VP2 transgenic CD4+ T cells were activated with 1 µg/mL anti-CD28 and 10 µg/mL anti-CD3 plate-bound antibody in the presence of 20 ng/mL rhTGF-β1 100 U rhIL-2 for 4 d. (B) In vitro generation of VP2-specific FoxP3+CD4+ T cells in the presence or absence of VP272-86 peptide in the presence of the above retinoic acid and cytokine mixture. (C) The function of VP2-TCR-Tg FoxP3+CD4+ T cells (103–105) activated in vitro was assessed with the inhibition of cytokine production of VP2-TCR Tg CD4+ T cells (5 × 105) upon stimulation with the epitope peptide (VP272-86). The VP2-TCR-Tg FoxP3+CD4+ T cells were purified from the spleens of FoxP3/GFP-Tg SJL mice crossed to VP2-TCR-Tg SJL mice for in vitro activation. The in vitro activated FoxP3+CD4+ T cells for 4 d were further sorted for GFP+ Tregs using MoFlo (Dako Cytomation, Glostrup, Denmark). * p < 0.05 and *** p < 0.0001. +, presence and −, absence of peptide.