FIGURE 4.
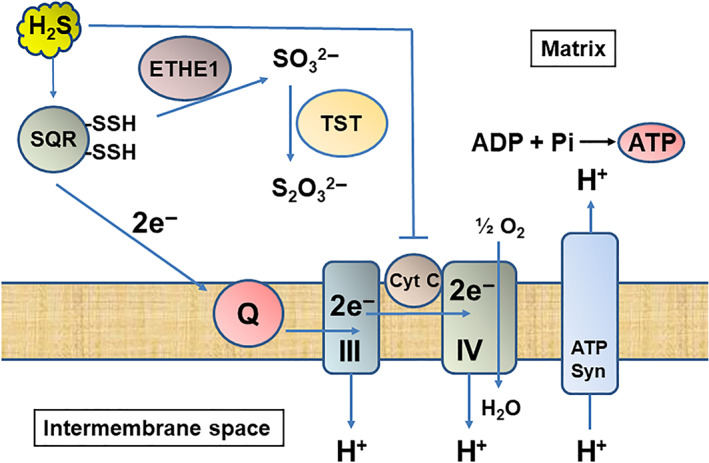
H2S is used for ATP production at physiological concentrations, while it inhibits cytochrome c oxidase at higher concentrations in mitochondria. H2S is metabolized by sulfur quinone oxidoreductase (SQR), sulfur dioxygenase (ETHE1, and rhodanese (TST) to thiosulfate through sulfite. Electrons are sent to coenzyme Q to complex IV through III and used for pumping out H+ from matrix to intermembrane space. ATP synthase produces ATP using the gradient of H+. In contrast, high concentrations of H2S suppress cytochrome c oxidase and the energy formation
