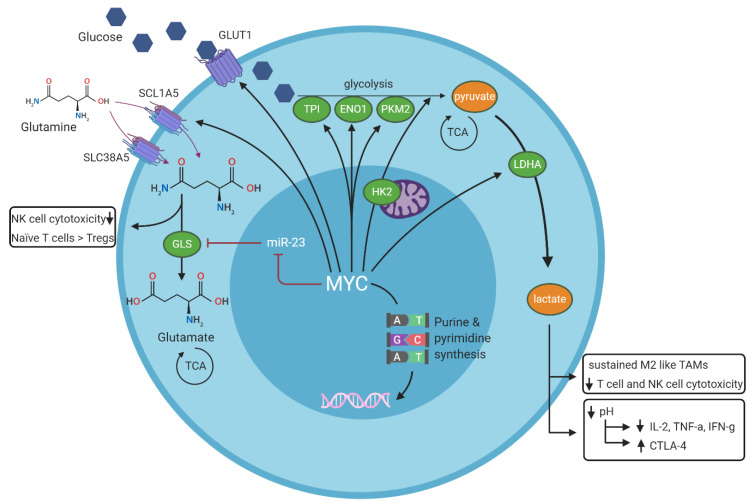
Figure 2.
Summary of MYC-dependent regulation of cell metabolism and its effects on the tumor immune environment. MYC stimulates aerobic glycolysis (the conversion of glucose into pyruvate) via glycolytic enzymes TPI, ENO1, PKM2 and HK, and MYC stimulates anaerobic glycolysis (the conversion of glucose into lactate) via LDHA. MYC stimulates glutaminolysis (the conversion of glutamine into glutamate) by inhibiting microRNA-23. Waste products of all three pathways contribute to decreased effector cell cytotoxicity in the tumor immune environment. Green ovals represent enzymes, dark red lines represent inhibitory signals and black arrows represent stimulatory signals. TPI = triose-phosphate isomerase, ENO1 = enolase 1, PKM2 = M2 isoform of pyruvate kinase, TCA = tricarboxylic acid (TCA) cycle, LDHA = lactate dehydrogenase A, TAMs = tumor associated macrophages, GLS = glutaminase, HK2 = hexokinase 2. GLUT1 = glycose transporter 1, SCL1A5 = solute carrier family 1 member 5 (or alanine serine cysteine transporter 2, ASCT2), SLC38A5 = solute carrier family 38 member 5 (or sodium-coupled neutral amino acid transporter 5, SNAT5).