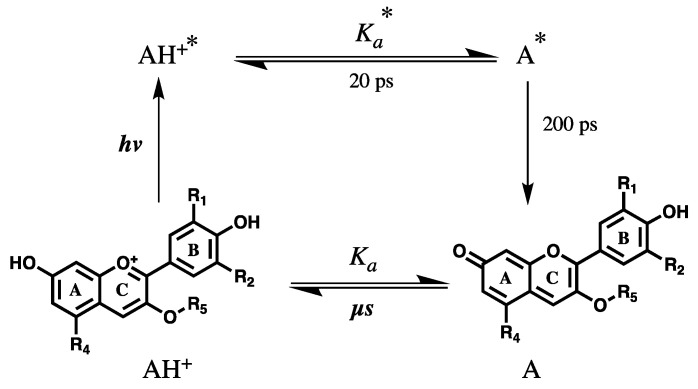
Figure 3.
Ground- and excited-state proton transfer process of anthocyanins. Absorption of light (hν) by the ground state cation form (AH+) produces the first excited singlet state of the cation (AH+*), which transfers a proton to water to form the excited singlet state of the conjugate base A*. The excited base form (A*) lives about 200 ps before transforming the excitation energy into heat and returning to the ground state of the base (A), which then reprotonates back to AH+ with no net chemistry. R1 = H, OH or OCH3; R2 = H, OH or OCH3; R4 = OH or sugar moiety; R5 = sugar moiety. The sugar moiety of anthocyanins can be composed by different attached molecules. The ESPT (acid dissociation constant in the excited state, Ka*) occurs on the picosecond time-scale and ground-state proton transfer (acid dissociation constant in the ground state, Ka) on the micro- to nanosecond time-scale.