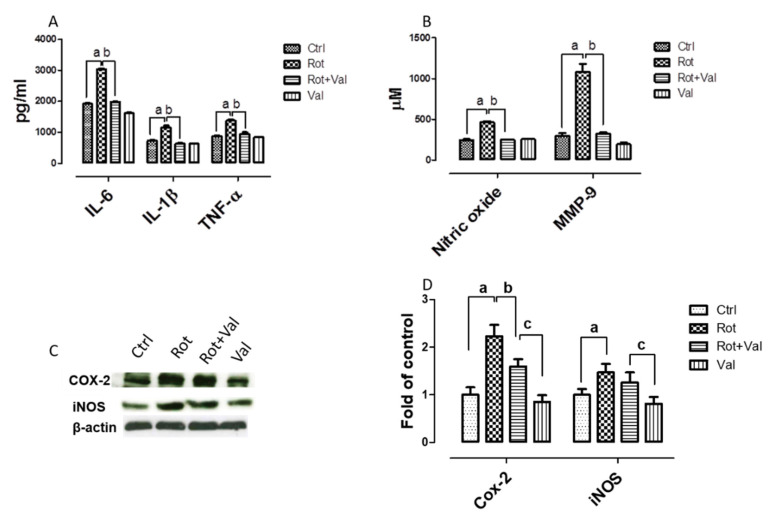
Figure 2.
Valeric acid prevented nitric oxide production and alters expression of inflammatory factors in rotenone treated animals. Enzyme linked Immunosorbent assay showed that rotenone administration increased the expression of pro-inflammatory cytokines (A) and enhanced production of NO and MMP-9 (B). Immunoblots of midbrain protein samples probed with Cox-2 and iNOS (C). Blots were quantified using Image J and corresponding results were represented as bar diagram (D). However, Val treatment caused a significant decrease in expression and production of pro-inflammatory factors in rotenone intoxicated animals. Data are expressed as mean ± SEM. a p < 0.05 compared to control, b p < 0.05 compared to rotenone treated group, c p < 0.05 compared to Rot+ Val treated group.