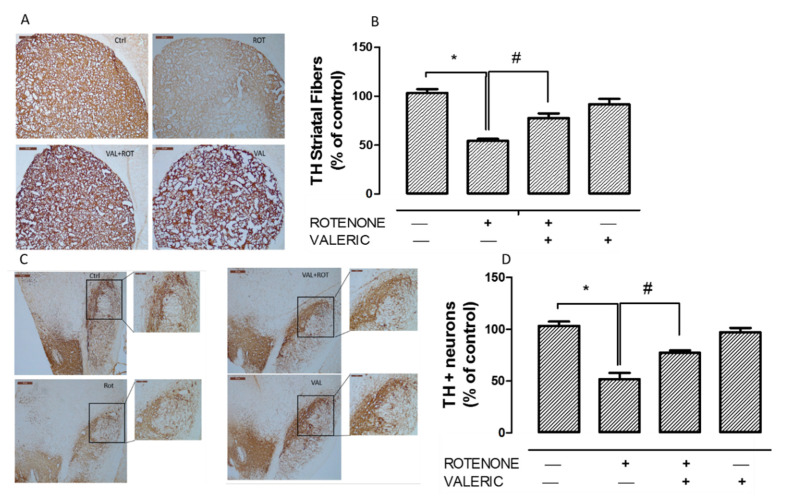
Figure 4.
Valeric acid attenuated rotenone induced dopaminergic neurodegeneration. Immunohistochemistry of 20 µm coronal sections with anti-tyrosine hydrolase antibody of striatum (A) and substantia nigra (B) of experimental animals. Densitometric analysis of tyrosine hydrolase positive neuronal fibers (C) and tyrosine hydrolase positive neurons (D) were performed using Image J. Administration of rotenone cause a significant reduction in both TH+ve neuronal fibers and neurons in striatum and substantia nigra respectively. Whereas, administration of Val prevented this loss significantly. Values are expressed as mean ± SEM. * p < 0.05 compared to control, # p < 0.05 compared to rotenone treated group.