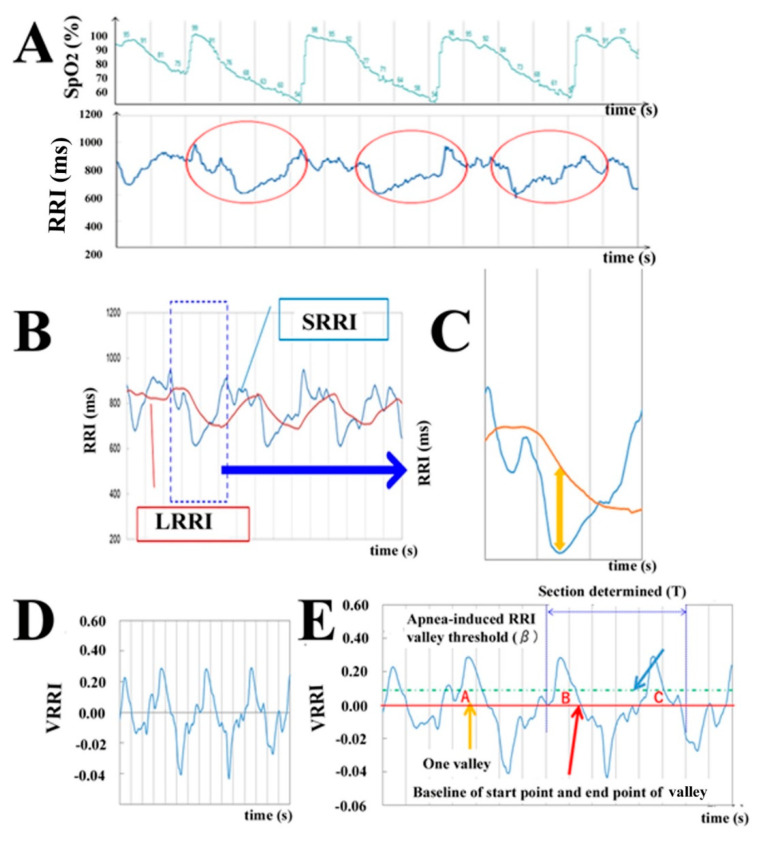
Figure 3.
Analysis of the R-R interval (RRI). (A) The graphs of SpO2 and RRI when apnea and CVHR occur. The horizontal axis indicates time, and the vertical axis shows SpO2 (%, upper trace) and RRI (ms, lower trace). Note that the occurrence of apnea and CVHR (shown by red circles) is repeatedly observed. (B) The method of measuring the depth of the RRI valley to detect the deep valley of the RRI in CVHR. The long average of RRI (LRRI) and short average of RRI (SRRI) were calculated from the RRI of 60 s and 5 s, respectively (details in Methods). (C) The large-scale graph of SRRI and LRRI at the location where CVHR occurs. The horizontal axis indicates time (s), and the vertical axis indicates RRI (ms). It can be seen that, considering LRRI minus SRRI as the depth of the valley, the deep valley of RRI caused by CVHR indicated by the orange arrow can be identified. (D) Depth of the valley of the RRI fluctuation (VRRI) at a certain time (t) corrected by LRRI2 (details in Methods). (E) VRRI during apnea. The depth VRRI exceeds the threshold (≥0.090) at three points: (A–C), in this case.