Figure 1.
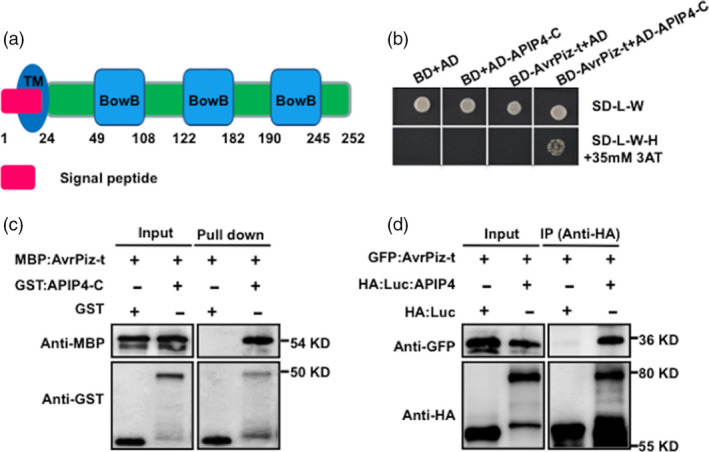
AvrPiz‐t targets APIP4 in vitro and in vivo. (a) The protein structure of APIP4. The position of the signal peptide, transmembrane domain and three BowB domains is indicated. (b) Interaction of AvrPiz‐t with APIP4‐C in yeast two‐hybrid assay. The growth of yeast colonies on the plate (SD‐L‐W‐H) lacking leucine (L), tryptophan(W) and histidine (H) with 35 mm 3‐aminotriazole (3 AT) indicates a positive interaction. 3 AT is a competitive inhibitor of the HIS3 gene product (histidine synthase), which is the reporter gene for the interaction in the yeast two‐hybrid assay. (c) Detection of the interaction of AvrPiz‐t and APIP4‐C in vitro with a GST pull‐down assay. MBP‐tagged AvrPiz‐t (MBP‐AvrPiz‐t) and GST‐tagged APIP4‐C recombinant proteins were expressed, and the protein–protein interaction was tested by a GST pull‐down assay. (d) Co‐IP assay of AvrPiz‐t and APIP4 in rice protoplasts. The AvrPiz‐t‐GFP and HA‐Luc‐APIP4 plasmids were used for co‐transfection of rice protoplasts. Protein isolated from rice protoplasts was immunoprecipitated with the anti‐HA antibody. Immunoblot analysis was performed using the anti‐HA and anti‐GFP antibodies.
