Figure 2.
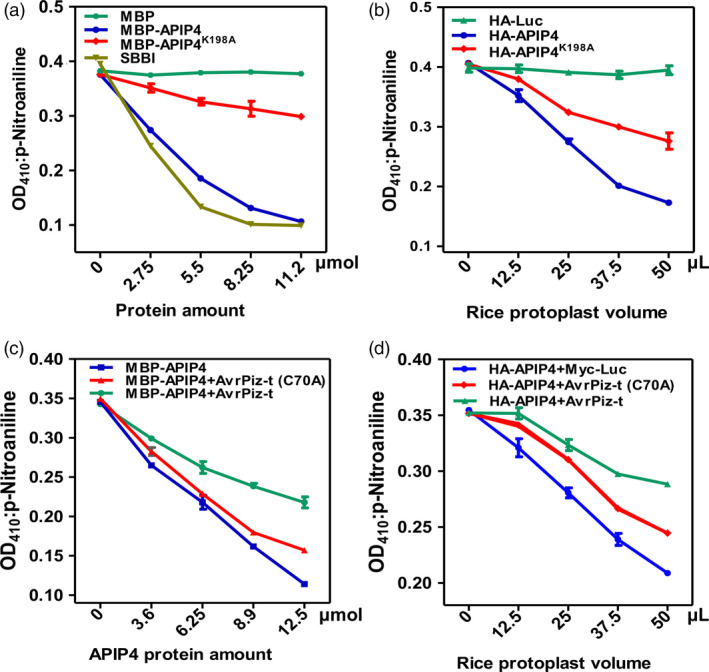
AvrPiz‐t interferes with APIP4 trypsin inhibitor activity in vitro and in vivo. (a) Trypsin inhibitor activity of APIP4 in vitro. The x‐axis indicates the protein amount. The y‐axis indicates the absorbance of p‐nitroaniline, the product of the trypsin in the reaction, at 410 nm. MBP was used as the negative control, and SBBI from soya bean was used as the positive control. (b) Trypsin inhibitor activity assay of APIP4 in vivo. HA‐Luc was used as the negative control. (c) Inhibition of APIP4 trypsin inhibitor activity by AvrPiz‐t in vitro. A trypsin inhibitor assay was performed by incubating increasing amounts of the APIP4 proteins and trypsin at 37°C for 20 min in the presence of about 12.5 µmol AvrPiz‐t and 12.5 µmol AvrPiz‐t (C70A). The x‐axis shows the protein amounts. (d) Suppression of APIP4 trypsin inhibitor activity by AvrPiz‐t in vivo. About 10 µg of plasmids HA‐APIP4 and Myc‐Luc, Myc‐AvrPiz‐t and Myc‐AvrPiz‐t (C70A) were used for co‐transfection into NPB protoplasts. Myc‐Luc was used as the negative control.
