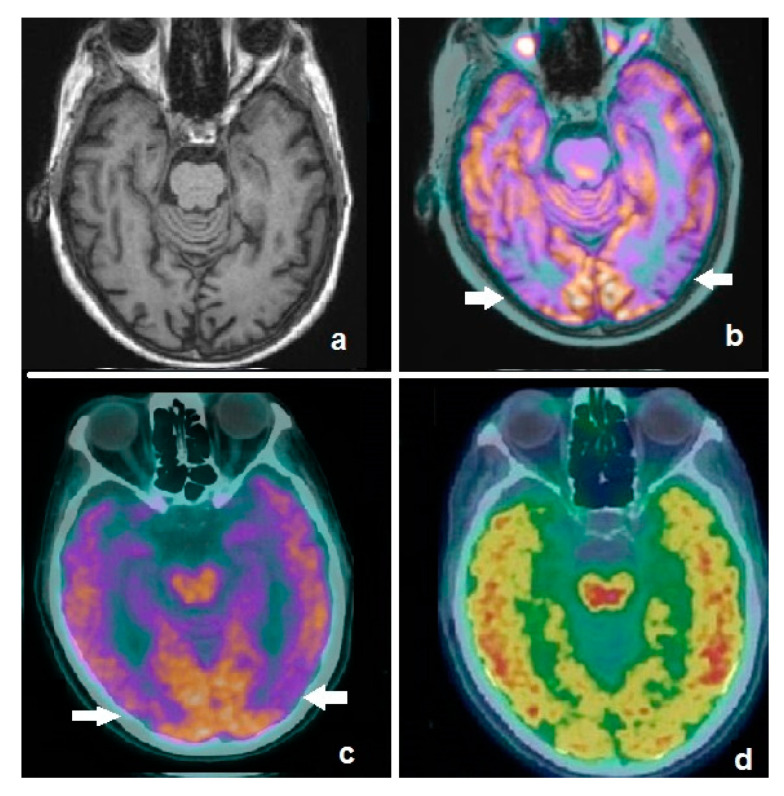
Figure 2.
Axial image of an MRI scan in a patient affected by mild cognitive impairment (a), showing no significant abnormalities. Fused corresponding 18F-FDG PET/MRI demonstrates hypometabolism in temporo-occipital lobes (b, white arrows). Patient was submitted to dual-phase amyloid PET with 18F-flutemetamol: the early phase demonstrates an AD-typical pattern (c, white arrows), substantially overlapping with the 18F-FDG findings, while the late phase shows pathological amyloid burden in the cortex (d). Dual-phase amyloid PET resulted to be useful for the simultaneous detection of neuronal dysfunction and amyloid burden.