Fig. 7. Aggregation in overexpressed LOXL1 and homolog mKATE2 sequences.
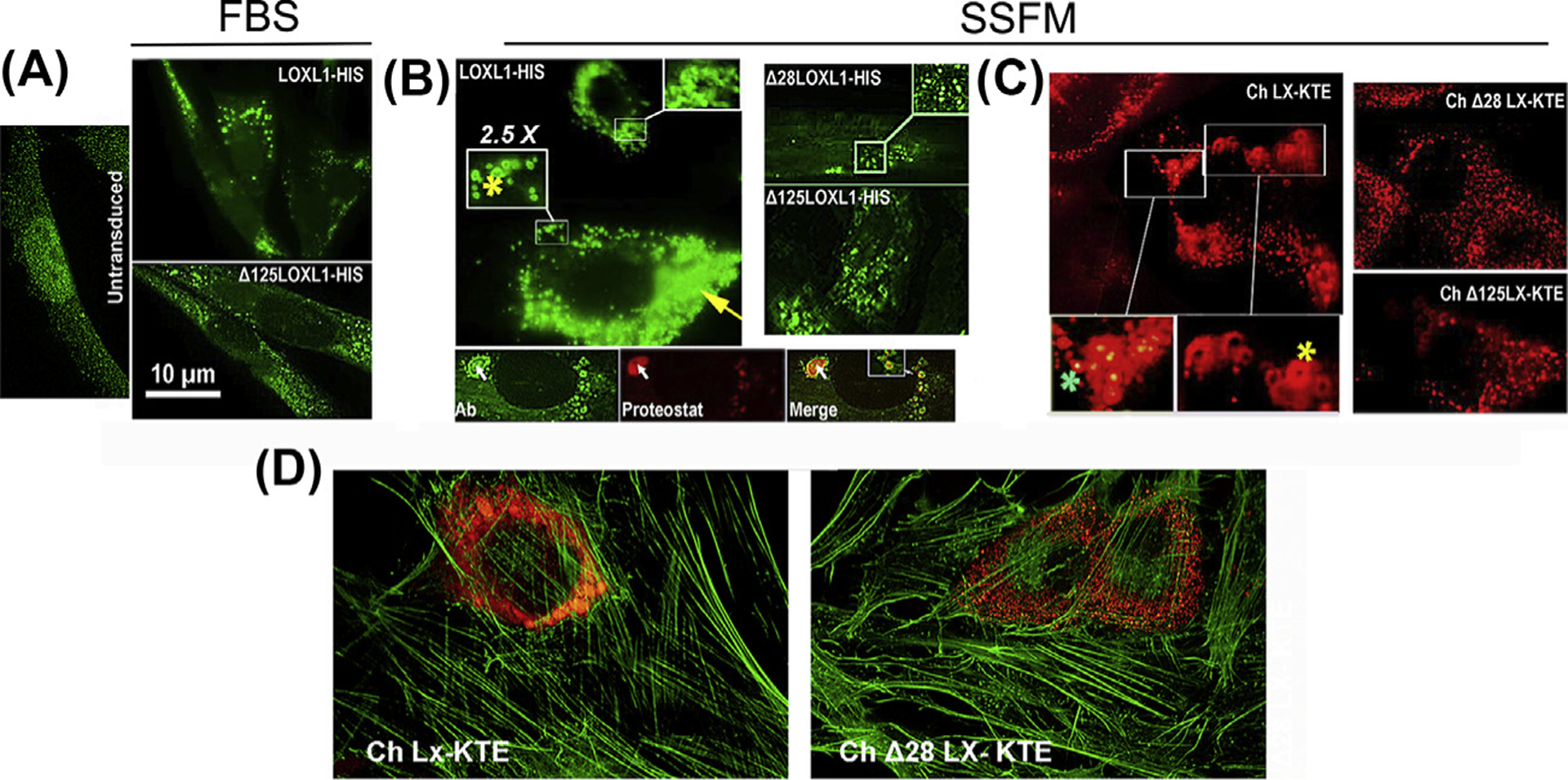
Representative images of BJ5a cells transduced with the indicated constructs. LOXL1 constructs were stained with an N-terminus anti-LOXL1 monoclonal Ab (H11 clone). Chimeras are red fluorescent. (A) Cultures in FBS-containing media. Left. Untransduced cells. Top. Cells transduced with LOXL1-HIS. Enlarged vesicles accumulated near the nuclei are the most common feature of cells expressing high levels of the transgene. Bottom. Typical stain profile for the Δ125–185 LOXL1 version. Vesicles are smaller and distribute throughout the cytosol. (B) Left top. The same transduction with LOXL1-HIS cDNA in supplemented-serum free media (SSFM). In addition to engorged vesicles (yellow arrow), very large particles and ring-shaped profiles (yellow asterisks) are frequent. Bottom 3-frame composite. Anti-LOXL1- Proteostat dual stain. Whereas the LOXL1 Ab stains the periphery of particles generating ring-shaped fluorescence, the aggregated-protein dye (Proteostat) labels the center of the same particles (white arrow). Right. LOXL1 with deleted domains lack this grossly vesicular phenotype. (C) The fluorescence patterns of the mKATE2 chimeras. Left. Ch LX-KTE fluorescence. Large vesicles and ring-like profiles (yellow asterisk) and engorged vesicles. There are also vesicles where the fluorescence intensity is higher at the center, rather than absent or lower (green asterisk). Right. The fluorescence of Δ versions. There are no aggregation profiles. (D) Micrographs of cells transduced with whole sequence (1–324) mKATE2 chimera and a chimera with a 28–95 aa deletion (Δ28) and counterstained with FITC-phalloidin.
