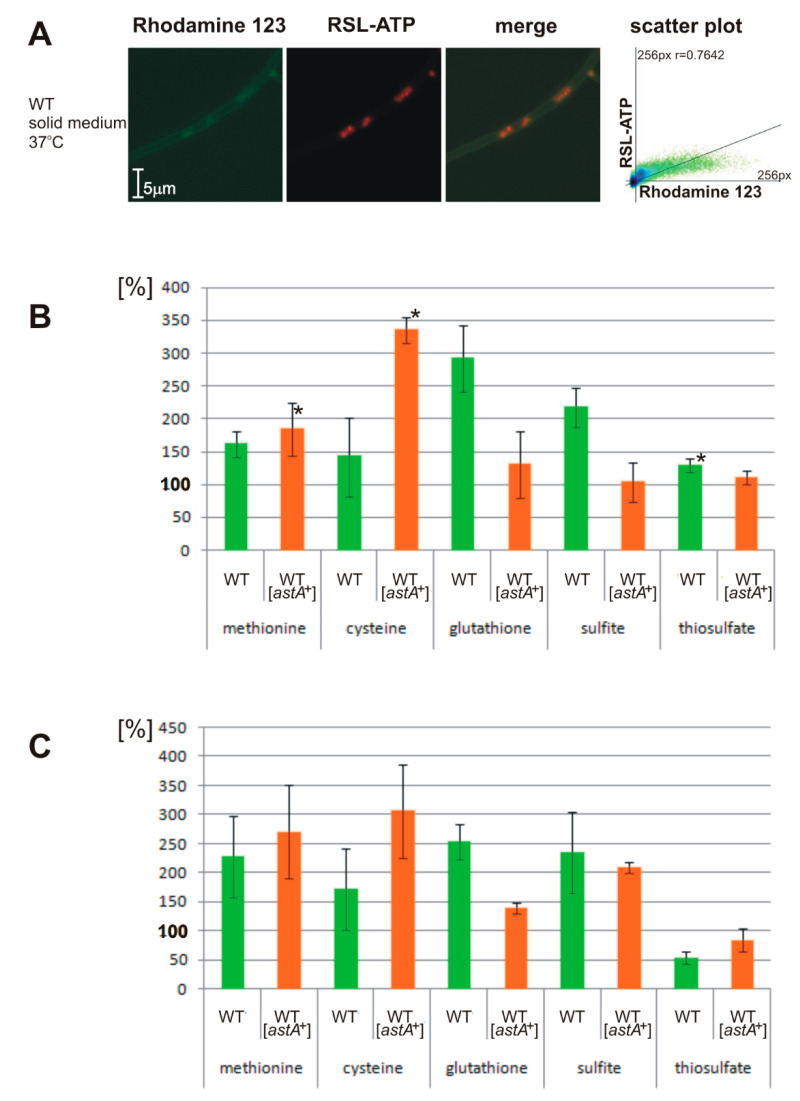
Figure 5.
ATP levels and sulfite oxidase (SOX) activity in astA-overexpressing strain depend on sulfur sources. (A) Representative visualization of RSL-based detection of ATP, which is localized mostly in the mitochondria. (right) Scatter plot and Pearson’s coefficient of two fluorescent signals. (B) Relative ATP amount or (C) SOX activity ratio (as a percentage, assuming 100% of ATP amount/SOX activity in the wild-type strain grown on 1 mM sulfate, final oxidation product of sulfur compounds in the mitochondria) in crude extracts of the wild-type and astA-overexpressing strain, cultured on media supplemented with 1 mM: methionine, cysteine, glutathione, sulfite, or thiosulfate. Values correspond to mean of three independent experiments and SD. *, statistically significant results compared to control (1 mM sulfate) by Student’s t-test with p-value < 0.05.