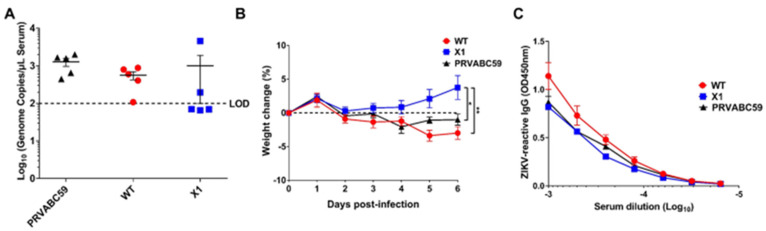
Figure 3.
X1 infection compared to WT Clone and ZIKV PRVABC59 in adult Ifnar1−/− mice. Male and female Ifnar1−/− mice 5–7 weeks in age were infected via intraperitoneal (IP) injection with 1e4 FFU of X1, WT ZIKV Clone, or PRVABC59 virus. (A) Serum samples were collected via retro-orbital (RO )bleed at 2 days post infection (DPI) to quantify early viral infection. RNA was isolated from the sera and used to detect ZIKV genome via RT-qPCR. Dotted line represents the limit of detection (LOD), no significant differences were found using Mann-Whitney tests to compare between viral infections (n = 5). (B) The weight of infected mice was monitored during acute infection and shown here as the percent of weight change relative to the baseline set at 0 DPI. Dotted line symbolizes 0% weight change. Two-way ANOVA was used to make multiple comparisons at each time point, asterisks representative of the following: * X1 vs. PRVABC59: p = 0.0464 at 5 DPI and p = 0.0014 at 6 DPI. ** X1 vs. WT: p < 0.0001 at 5 and 6 DPI. (n = 5). (C) Serum was collected via cardiac stick at 20 DPI to detect a ZIKV-reactive antibody response. ZIKV-reactive IgG was detected by indirect ELISA using ZIKV virions as antigen and donkey α mouse IgG HRP conjugate as detecting antibody. Data shown as optical density (OD) at various serum dilutions, normalized with uninfected mouse sera (n = 2, NS).