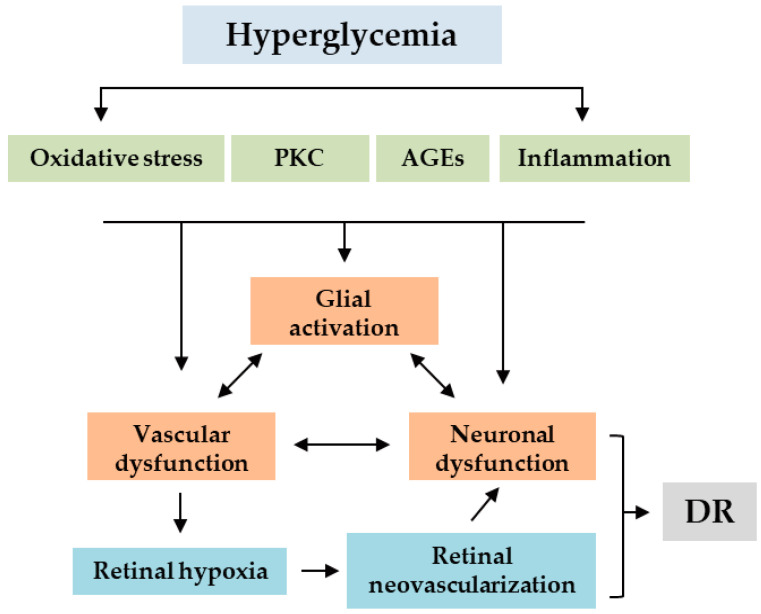
Figure 1.
Schematic presentation of pathogenic mechanisms of diabetic retinopathy (DR). Hyperglycemia-induced metabolic stresses, such as mitochondrial oxidative stress, activation of protein kinase C (PKC) pathway, accumulation of advanced glycation end products (AGEs) and inflammation, induce impairment of crosstalk between neurons, glia and vasculatures through glial activation, vascular dysfunction and neuronal dysfunction. Retinal hypoxia induced by vascular dysfunction causes retinal neovascularization which worsens neuronal dysfunction in the retina, finally leading to DR. Double-headed arrows, interlinking process of events; single-headed arrows, one-way direction process of an event to the other event.