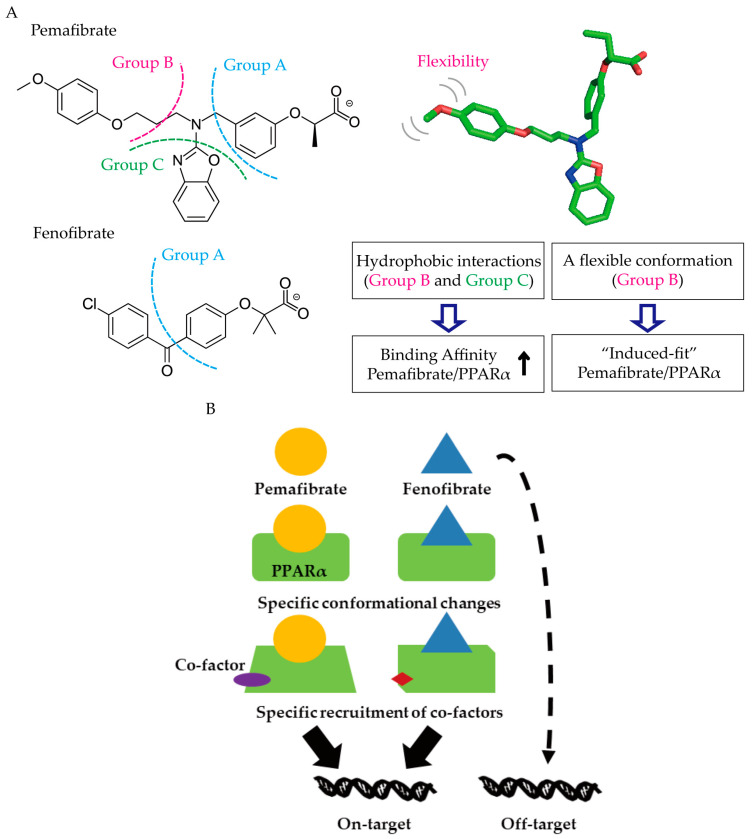
Figure 2.
Structural differences between pemafibrate and fenofibrate. (A) The structure of pemafibrate contains the carboxylic acid group (Group A, blue color), phenoxy alkyl group (Group B, red color) and 2-aminobenzoxasole group (Group C, green color) while that of fenofibrate only contains Group A. This hydrophobic Y-structure of pemafibrate (Group B and C), which interacts with the hydrophobic residues in the ligand-binding pocket of PPARα, results in the improvement of fitting with the ligand-binding pocket of PPARα via increasing the receptor-ligand binding affinity. The flexibility of Group B confers the stronger “induced fit” conformation with PPARα. (B) The specific binding of pemafibrate can induce specific conformational transitions of PPARα with specific co-factor complexes resulting in exerting the on-target effects of PPARα activation while that of fenofibrate could exert the on-target as well as off-target effects other than PPARα activation such as deleterious effects on the renal function including increased serum creatinine levels. Solid lines: a direct series of an event; A dotted line: an indirect series of an event.