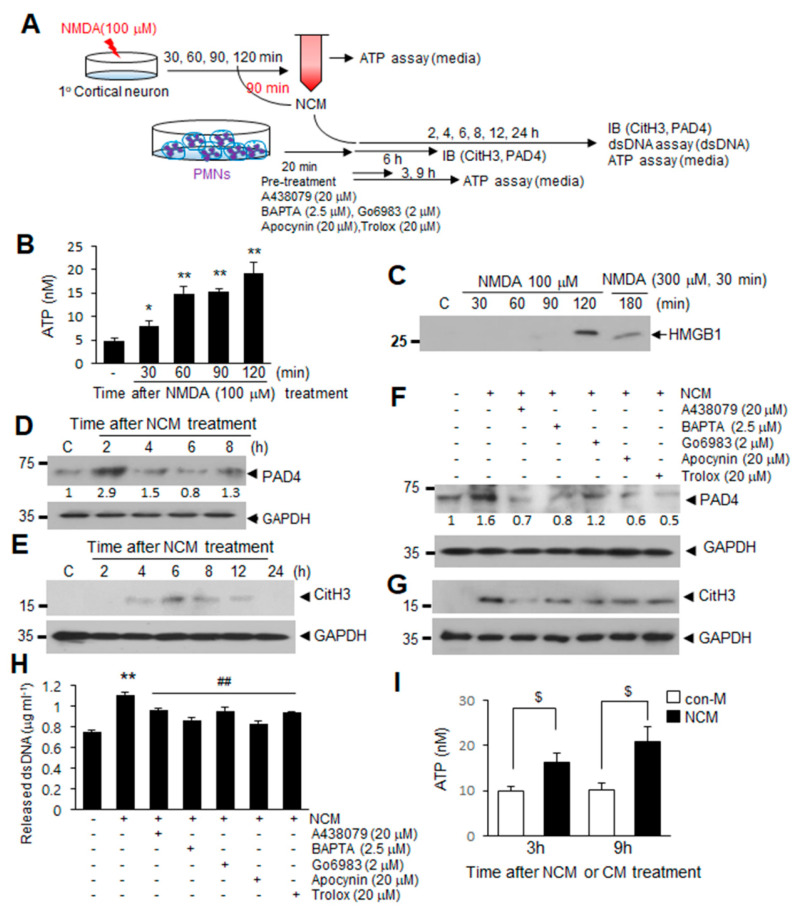
Figure 5.
ATP release after excitotoxic neuronal cell death induces NETosis via a P2X7R-Ca2+-PKC signaling pathways. (A) Primary cortical neuron cultures were treated with 100 μM NMDA for various duration. NMDA-conditioned media (NCM) was prepared after 90 min of NMDA treatment and used to treat blood PMNs. (B) Primary cortical neuron cultures were treated with 100 μM NMDA for 30, 60, 90, or 120 min, and the ATP levels in primary cortical neuron culture media were subsequently measured using an ATP assay kit. (C) HMGB1 levels in culture media were determined after treating primary cortical neurons with NMDA (100 μM) for 30, 60, 90, or 120 min by immunoblotting. (D,E) Levels of PAD4 and CitH3 in NCM-treated blood PMNs were determined at the indicated times by immunoblotting. (F,G) Blood PMNs were pretreated with A438079 (20 μM), BAPTA (2.5 μM), Go6983 (2 μM), apocynin (20 μM), or Trolox (20 μM) for 20 min prior to treatment with NCM for 6 h, with the levels of PAD4 and CitH3 subsequently determined using immunoblotting. Immunoblots are representative of 2~4 independent experiments. (H) dsDNA release was measured after pretreating blood PMNs with A438079 (20 μM), BAPTA (2.5 μM), Go6983 (2 μM), apocynin (20 μM), or Trolox (20 μM) for 20 min prior to treatment with NCM. (I) Blood PMNs were treated with NCM or NMDA-untreated control media (con-M) for 3 or 9 h, and ATP levels in culture media of blood PMNs were determined using an ATP assay kit. Results are presented as mean ± SEM (n = 3). ** p < 0.01, * p < 0.05 versus the PBS-treated controls, ## p < 0.01 versus NCM only-treated cells, $ p < 0.05 between indicated group. Numbers under the blot indicate band intensities.