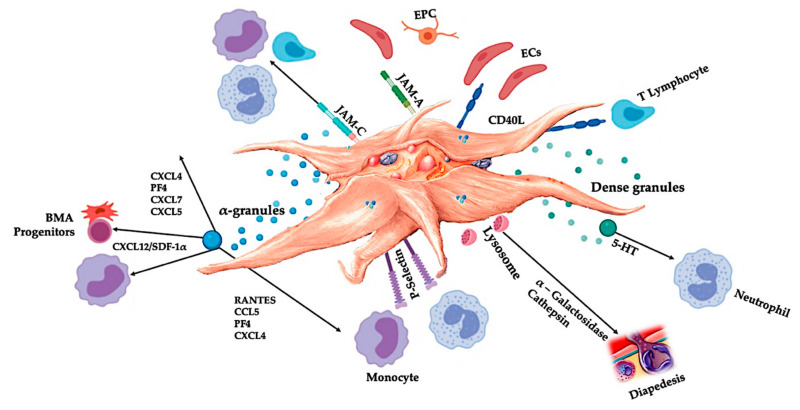
Figure 3.
Activated platelets, releasing PGF, and adhesion molecules mediate a variety of cellular interactions: chemotaxis, cell adhesion, migration, cell differentiation, and stipulate to immunomodulatory activities [67,68]. These platelet cell-cell interactions contribute to angiogenesis [46,69,70] and inflammatory [71,72] activities, ultimately to stimulate tissue repair processes. Abbreviations: BMA: bone marrow aspirate, EPC: endothelial progenitor cell, EC: endothelial cells, 5-HT: serotonin, RANTES: Regulated upon Activation Normal T Cell Expressed and Presumably Secreted, JAM: junctional adhesion molecules type, CD40L: cluster of differentiation 40 ligand, SDF-1α: stromal cell-derived factor 1 alpha, CXCL: chemokine (C-X-C motif) ligand, PF4: platelet factor 4. Adapted and modified from Everts et al. [9].