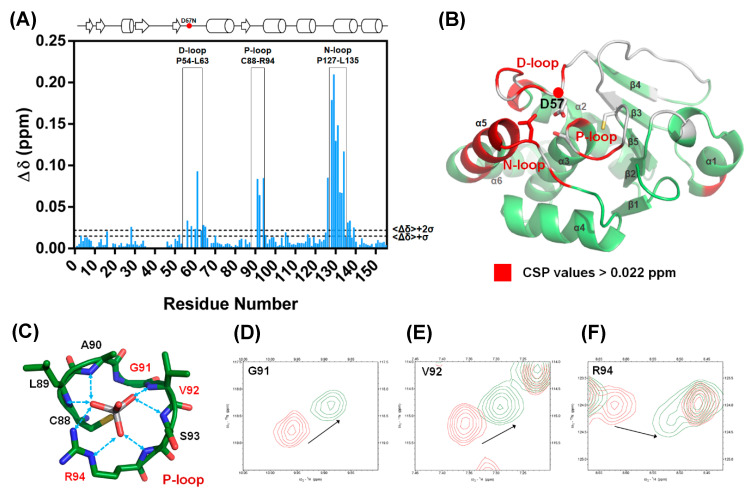
Figure 3.
The D57N mutant exhibited a perturbed conformation as a result of DPN–triloop interactions. (A) The catalytic residue, D57, was replaced with asparagine, and the chemical shift perturbation (CSP) values were calculated. The threshold was set at Δδ + 2σ, and the value was 0.022 ppm. The data indicated that the residues in the D-loop, P-loop, and N-loop were specifically perturbed by the D57N mutant. (B) The residues with CSP values greater than Δδ + 2σ are labeled on the DUSP22 structure in red. These results revealed the region that was perturbed by DPN–triloop interaction, including the D-loop, P-loop, N-loop, and α-helix 5 (α5). The spaces and white residues were non-assigned residues in the backbone assignment, including proline and disappeared signals in the 3D spectra. (C–F) The P-loop is the binding site, and the residues in the P-loop share their backbone amides as well as side chains to interact with the ligands. The 1H-,15N-HSQC spectrum of the WT (red) was superimposed with the spectrum of D57N (green) to show that the P-loop residues, G91, V92, and R94, were perturbed by disruption of the DPN–triloop interaction.