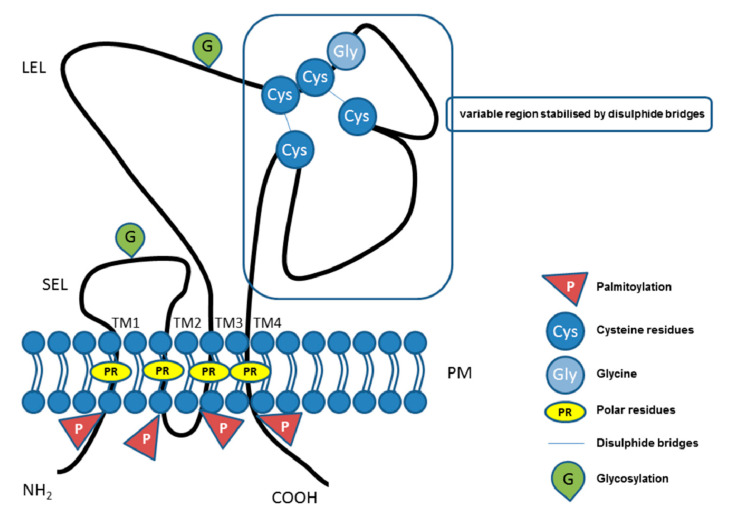
Figure 2.
Illustrative schema of tetraspanin structure. Tetraspanin proteins traverse the plasma membrane (PM) four times, thus, defining the four transmembrane domains (TM1, TM2, TM3, TM4) with conserved polar residues (PRs) in their structure. In the extracellular space, the small (SEL) and large (LEL) extracellular loops can be recognized. The LEL contains a highly conserved CCG motif and possibly an additional two, four, five, six, or eight conserved cysteine residues (Cys). Between the cysteine residues, two disulfide bridges that enable folding of the LEL can be formed. Tetraspanins are post-translationally modified by glycosylation (G) in the large or small extracellular domain and palmitoylation (P) at the intracellular cysteine residues. Short N-terminal and C-terminal tails are oriented intracellularly.