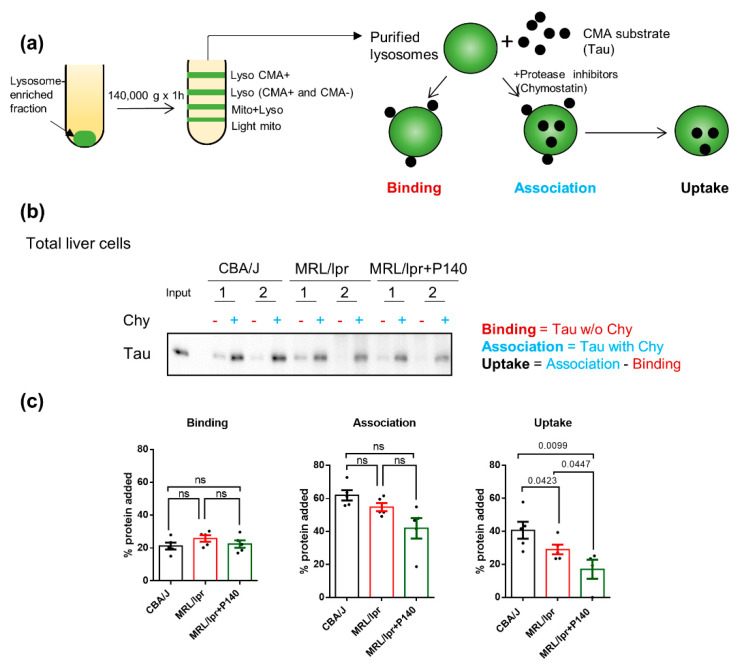
Figure 3.
Effect of P140 peptide on the uptake of a prototypical chaperone-mediated autophagy (CMA) substrate into CMA-active lysosomal liver preparations. (a) Schematic presentation of purification of lysosomes and incubation assay to measure translocation of CMA uptake in vitro. Lysosome fractions with high (+) CMA activity were prepared from the liver of CBA/J, MRL/lpr and P140-treated MRL/lpr mice. Recombinant Tau protein (0.2 μg) was added for 20 min at 37 °C to lysosomes previously treated or not with the protease inhibitor chymostatin (chy; 100 μM for 10 min at 0 °C and diluted to a final concentration of 33 μM). Samples were subsequently treated for analysis by SDS-PAGE and Western blotting. (b) Western blots of the levels of Tau recovered from CMA+ lysosomes in the presence or not of chymostatin from the livers of CBA/J, MRL/lpr and P140-treated MRL/lpr mice. (c) Evaluation of the binding, association and uptake of Tau to CMA+ lysosomes recovered from the livers of the three mice groups, by using densitometry of the blots shown in (b). Five samples (each represented by one point) were examined for each study group. Each point represents a sample pooled from 2–3 livers. One-way ANOVA Krustal-Wallis test was used to analyze the statistical significance. Error bars are ± SEM. ns means p values > 0.05.