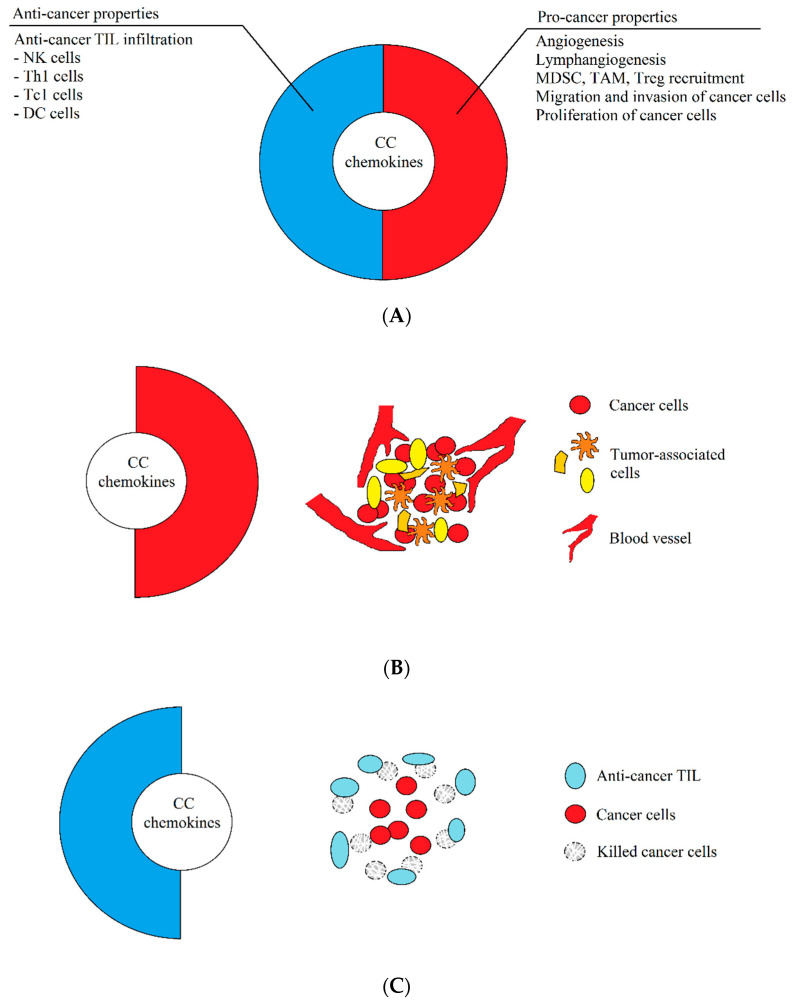
Figure 1.
The dual properties of CC chemokines. (A) Most, if not all, the chemokines described in this paper have both pro- and anti-cancer properties. The anti-cancer properties consist of the recruitment of anti-cancer tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes (TIL), which infiltrates the tumor and destroys tumor cells. The pro-cancer properties of chemokines, on the other hand, consist in causing angiogenesis and lymphangiogenesis, recruitment of pro-cancer cells supporting the development of the tumor, and the stimulation of proliferation, the induction of migration, and the invasion of cancer cells. (B) In a growing tumor, CC chemokines have enhanced pro-cancer properties, while anti-cancer properties are suppressed. As a result, these chemokines participate in the development of a tumor by causing angiogenesis, migration of tumor cells, and recruitment of cells supporting the development of a tumor, which results in the progress of cancer. (C) During immunotherapy or an effective anticancer response of the immune system, the same CC chemokines show enhanced anti-cancer properties, which result in the infiltration of a tumor by anti-cancer TIL, which destroy tumor cells. The immune system fights with the tumor, which often leads to recovery.