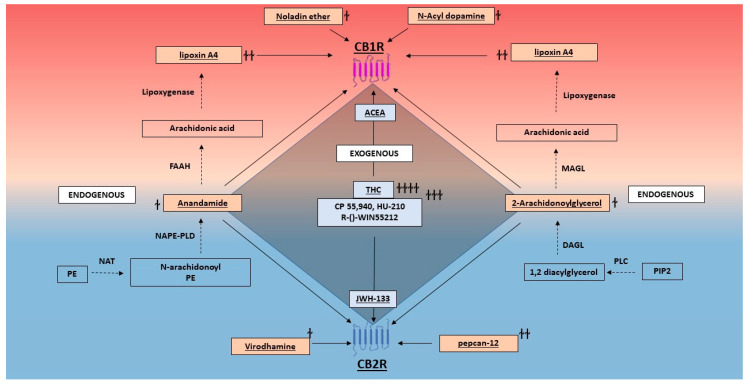
Figure 1.
Overview of endogenous and exogenous cannabinoids that activate/modulate CB1R and CB2R. An overview of CB1R activators and modulators are shown in this figure. This includes endogenous (ɫ,ɫɫ), and exogenous (ɫɫɫ,ɫɫɫɫ) ligands. Examples of endogenous ligands listed here are the endocannabinoids (2-AG, anandamide, N-acyl dopamine, noladin ether and virodhamine (ɫ)); endogenous positive allosteric modulators (lipoxin A4 and pepcan-12 (ɫɫ)); synthetic exogenous cannabinoids for CB1R (ACEA (ɫɫɫ)), CB2R (JWH133 (ɫɫɫ)) and both (CP 55,940, HU-210 and R-()-WIN55212 (ɫɫɫ)); and phytocannabinoids (Δ9-tetrahydrocannabinol (ɫɫɫɫ)). (PE: phosphatidylethanolamine; NAT: N-acetyltransferase; NAPE-PLD: N-acyl phosphatidylethanolamine phospholipase D; FAAH: fatty acid amide hydrolase; PIP2: phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate; PLC: phospholipase C; DAGL: diacylglycerol lipase; MAGL: monoacylglycerol lipase; ACEA: arachidonyl-2′-chloroethylamide; THC: Δ9- tetrahydrocannabinol).