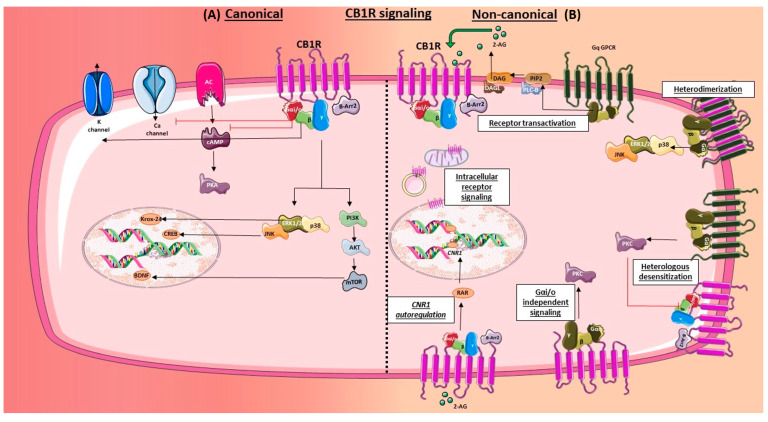
Figure 3.
Canonical and non-canonical signaling of CB1R. (A) Canonically, CB1R activation results in coupling of pertussis toxin (PTX)-sensitive G-protein (Gαi/o), and the activation of GIRK and inhibition of calcium channels. CB1Rs also activate MAPKs, such as ERK1/2 and JNK, which result in the subsequent induction of Krox-24 and CREB respectively. In addition, CB1R stimulation also leads to the downstream activation of PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway, which further results in the transcription of BDNF. (B) The CB1R is also involved in non-canonical signaling. Gαq/11 GPCR-mediated-mobilization of endocannabinoids, and subsequent activation of the CB1R in an autocrine or paracrine fashion (Receptor transactivation). The CB1R has also been shown to dimerize with other GPCRs resulting in a change in CB1R-mediated signaling, such as changes in MAPK activation patterns (Heterodimerization). Additionally, GPCRs that activate PKC, such as Gαq/11 GPCRs, have also been shown to phosphorylate CB1R and potentially dampen its activity in certain cell types (heterologous desensitization). Certain cannabinoids have been shown to couple to Gαq/11 and Gα(s) proteins, and effectively activate calcium channels (Gαi/o independent signaling). In addition to being membrane-bound, functional CB1R has also been reported to localize intracellularly, such as the nucleus and the mitochondria, where they are capable of signaling (intracellular signaling). Finally, cannabinoids have been shown to trigger an induction of CNR1 by the activation of CB1R in various cell types (autoinduction). (AC: adenylyl cyclase; cAMP: cyclic adenosine monophosphate; PKA: protein kinase A; β-Arr2: Beta-arrestin-2; ERK1/2: extracellular signal-regulated kinases; JNK: c-Jun N-terminal kinases; PI3K: phosphoinositide 3-kinases; AKT: protein kinase B; mTOR: mammalian target of rapamycin; PIP2: phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate; PLC-β: phospholipase C beta; DAG: diacylglycerol; DAGL: diacylglycerol lipase; 2-AG: 2-arachidonoylglycerol; RAR: retinoic acid receptor; CNR1: cannabinoid receptor 1 gene).