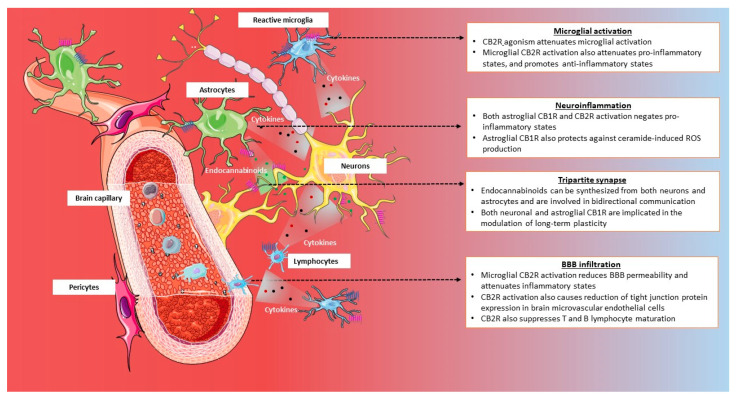
Figure 4.
Regulation of synaptic activity and neuroinflammatory states by cannabinoid receptors. CB2R located on both microglial and astroglial cells are involved in the attenuation of inflammatory states. They do so by inhibition of microglial activation, reduced secretion of pro-inflammatory cytokines, and increased secretion of anti-inflammatory cytokines, and limiting the infiltration of peripheral immune cells. The CB2R is also expressed in the brain microvascular endothelial cells whereby they regulate expression of tight junctions, and further limit chemotaxis and transmigration of peripheral immune cells into the CNS. The CB2R also limits T- and B-cell proliferation and immunomodulation. Astroglial CB1R also promotes an anti-inflammatory state while simultaneously lowering levels of pro-inflammatory cytokines. Additionally, both neuronal and astroglial cells secrete endocannabinoids which are involved in modulation of synaptic strengthening by LTP and LTD. Additionally, astroglial CB1R activation has also been demonstrated to protect against excitotoxic neuronal damage and some forms of neurotoxic damage.