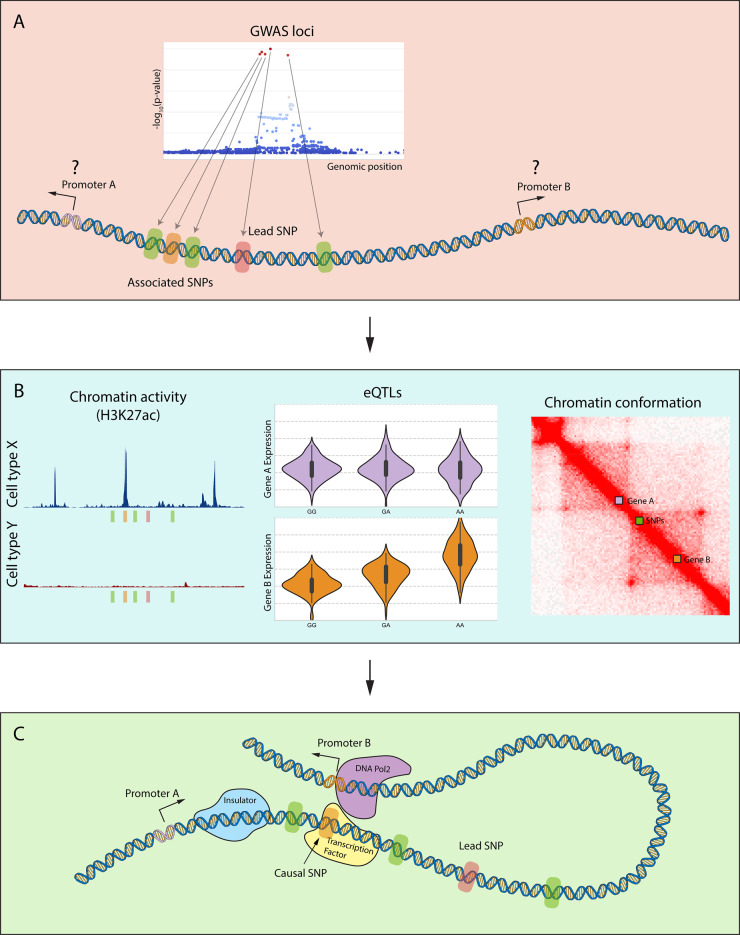
Fig. 1.
Using functional genomics to describe GWAS loci
(A) A typical GWAS loci usually consists of many variants in high linkage disequilibrium and frequently far away from any genes, which can make the interpretation of the association challenging. (B) It is possible to use a combination of functional genomics techniques to study these loci, such as: chromatin activity to identify which SNPs are functionally relevant and in which cell types; eQTLs to correlate genotype with changes in gene expression; and chromatin conformation to identify regulatory domains that determine which genes can be affected. (C) These methods combined with others allow us to identify the functional importance of GWAS associations in the disease.