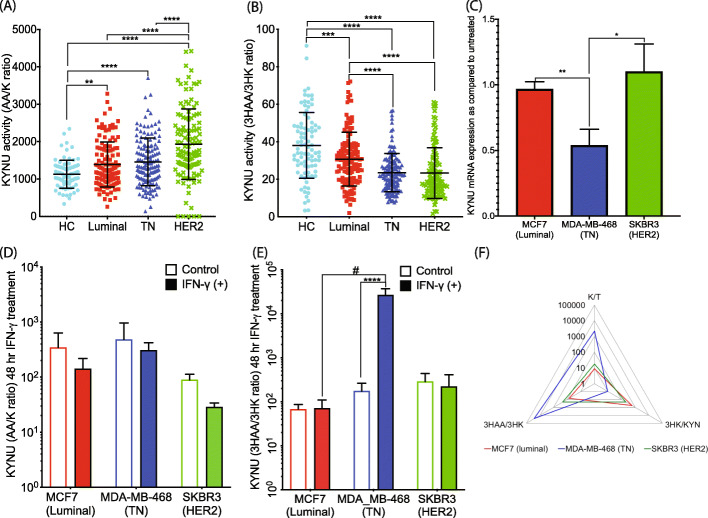
Fig. 5.
KYNU is dysregulated in HER2-enriched and TN BrCa subtype. a KYNU activity along the minor KP sub-branch leading to AA (as reflected by the AA/K ratio) is upregulated in all BrCa patient sera relative to HC, with HER2-enriched BrCa patient serum showing the highest KYNU activity in this sub-branch. b KYNU activity along the major KP sub-branch that leads to 3HAA (as reflected by the 3HAA/3HK ratio) is downregulated in all BrCa patient sera relative to HC, with HER2-enriched BrCa patient serum showing the lowest KYNU activity in this sub-branch. c KYNU mRNA expression is not induced in TN BrCa cells after 24 h IFN-γ treatment (n = 3, in triplicates) relative to untreated cells. d KYNU activity along the minor KP sub-branch that leads to AA (as reflected by AA/K ratio) does not significantly change in BrCa cell lines after 48 h IFN-γ treatment, whereas e KYNU activity along the major KP sub-branch leading to 3HAA (as reflected by 3HAA/K ratio) is significantly upregulated in TN BrCa cells lines after 48 h IFN-γ treatment. f Radar chart of KP enzyme activity after IFN-γ treatment (as reflected by various KP metabolite ratios) shows the distinct pattern of KP dysregulation in TN BrCa cells, relative to luminal and HER2-enriched BrCa cells (increased IDO1 and major sub-branch KYNU activity) which, in turn, leads to the preferential production of the immune-suppressive metabolite 3HAA. KP metabolite analysis was performed using uHPLC in BrCa cell supernatants and cell pellets (n = 3, in triplicate) or in human plasma samples, HC (n = 98), luminal (n = 138), TN (n = 143), and HER2-enriched (n = 127). The error bars in c–e indicate the standard deviation from the triplicates of cell culture treatment. *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01; ***p < 0.001; ****p < 0.0001