Fig 3.
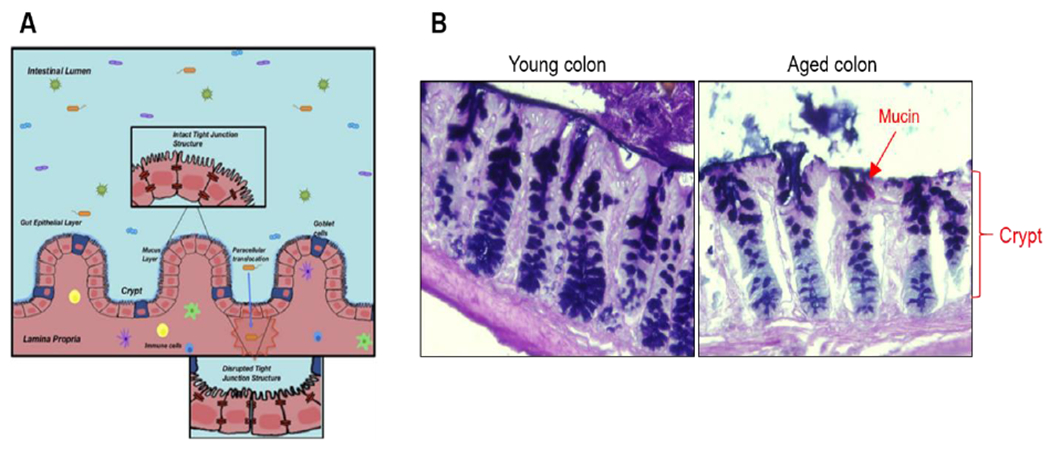
(A) Disruption in gut epithelial structure may allow the translocation of commensal bacteria and toxic signals into the host which cause both inflammation and infection. (B) Age-associated impairment of the histological architecture and the mucin production in the colon. Colonic tissues were collected from young (2-3 months) and aged (18-20 months) mice and stained with Alcian-blue and periodic acid-Schiff staining to examine the global structure and mucins.
