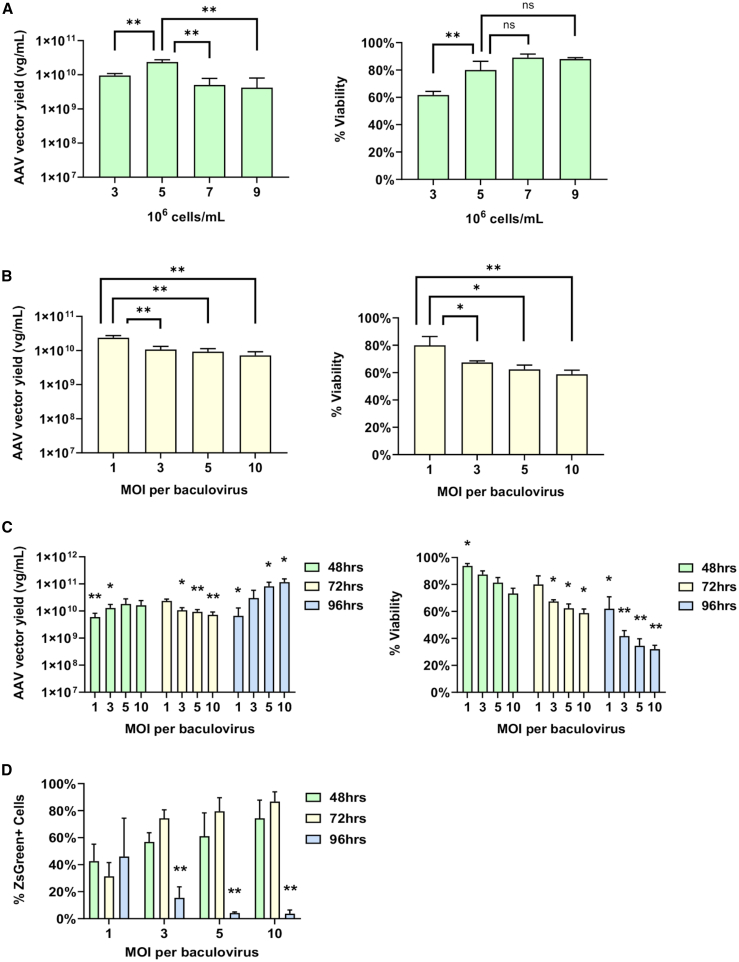
Figure 2.
Optimization of AAV Production in ExpiSf Expression System
(A) Infection with varying cell densities (cells/mL) at the time of infection was tested using an MOI of 1 per baculovirus (left panel). qPCR was used to measure the viral genomes per milliliter (vg/mL) of each sample. Percentage of viable cells (% viability) was monitored during the optimization of the cell density (right panel). (B) Infection with varying MOIs of the baculoviruses was tested using a cell density of 5 × 106 cells/mL (left panel). qPCR was used to measure the titers (vg/mL). Percentage of viable cells (% viability) was monitored during the optimization of the MOI (right panel). (C) Infection with varying MOIs of the baculoviruses was tested using a cell density of 5 × 106 cells/mL (left panel). Samples were taken at 48 h, 72 h, and 96 h postinfection. qPCR was used to measure the titers (vg/mL). Percentage of viable cells (% viability) was monitored during the optimization of the MOI and harvest time (right panel). For statistical analysis, each condition was compared to the 72-h MOI of 1 condition. (D) Crude cell lysates of AAV2 produced with varying baculoviral MOIs were harvested at 48 h, 72 h, and 96 h postinfection. The infectivities were assessed by transducing Ad293 cells with a MOI of 100. The percentage of ZsGreen-positive cells was measured by flow cytometry. Statistical analysis was performed within each MOI group and was compared to its 72-h time point. ∗p < 0.05, ∗∗p < 0.005.