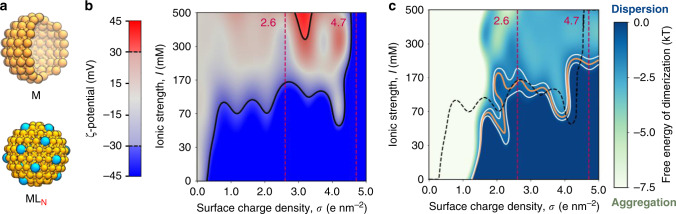
Fig. 2. Dispersion state phase diagrams of ion-capped metallic NPs.
a Coarse-grained models of pristine (M, top) and capped (MLN, bottom) NPs for the construction of the phase diagrams. The cyan beads implicitly account for grafted ligands with a charge of −2 e. b The relation between the NP surface charge density (σ), the environment ionic strength (I), and the computed ζ-potential. The black contour demarcates the region where the ζ-potential lies between −30 and +30 mV. The opaque blue and red regions indicate the conditions where the ζ-potential computations suggest colloidal stability. c Map of the NPs free energy of dimerization for the various studied systems. The orange and white curves outline the region where the free energy is −1.0 ± 0.5 kT. The black contour drawn for the ζ-potential is superimposed onto this plot. The dark blue and light green colors indicate the conditions at which the free energy calculations suggest colloidal stability and aggregation, respectively. The dashed, red lines indicate the limiting values of σ for citrate-capped NPs as determined by the developed theoretical model.