Figure 1.
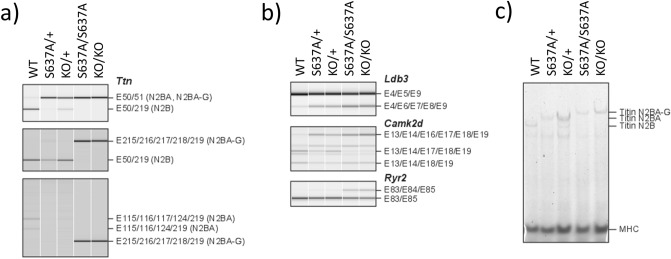
Rbm20S637A/S637A and Rbm20KO/KO mice are defective in RBM20-dependent alternative splicing. (a) RT-PCR analysis of Ttn mRNAs with exon (E) 50 forward, E51 reverse and E219 reverse primers (top), E50 forward, E215 forward and E219 reverse primers (middle) and E115 forward, E215 forward and E219 reverse primers (bottom). Splicing patterns of the PCR products and names of corresponding titin isoforms are indicated on the right. (b) RT-PCR analysis of Ldb3 (top), Camk2d (middle), and Ryr2 (bottom) mRNAs. Gel-like images by Bioanalyzer (Agilent) are shown (a,b). (c) Vertical SDS-agarose gel electrophoresis and CBB staining of cardiac proteins from the hearts of 4-week-old Rbm20 mutant mice. Genotypes of the individual mice are indicated above. Titin isoforms (N2B, N2BA and N2BA-G) and myosin heavy chain (MHC) are indicated. n = 3 mice (a–c), each showing similar results. Full length original images are shown in Supplementary Information.