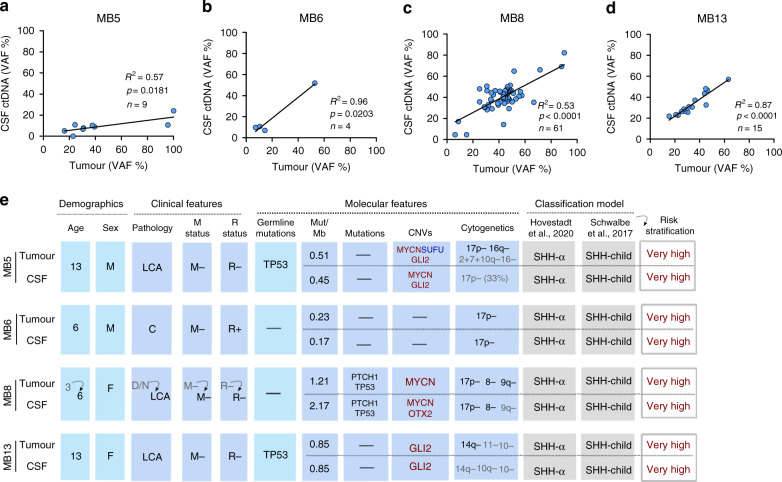
Fig. 3. WES of CSF ctDNA reveals the genomic alterations of the tumour and identifies MB-subgroup.
a–d Correlation of CSF ctDNA VAF with tumour VAF for each mutation identified in the tumour sample (VAF > 5%). Linear regression and Goodness-of-fit R2 indicated in each figure. n, represents the number of mutations detected in the primary tumour sample with VAF > 5%. e Clinicopathological characteristics and molecular alterations based on tumour and CSF ctDNA WES analysis. MB-subgroup classification and risk stratification (based on Schwalbe et al., 2017 5-year PFS). Frequency of somatic mutations in coding regions per Mb (Mut/Mb) based on a 17.7 Mb (MB5, MB6, MB13), 50.4 Mb (MB8-Tumour) and 51.6 Mb (MB8-CSF) WES panel. CNV: deletion (log2 value < −1, blue), amplification (log2 value > 1, red). For the cytogenetic analysis, the threshold for the percentage of arm-level or chromosome gain/loss was determined by the mean and the percentiles of the events from the cohort of 13 MB as indicated in Fig. 1: greater than 75% percentile (>65.5%) in black and greater than the mean (>44.5%) in grey. The definition of the symbols and acronyms are in accordance with Fig. 1 and are as follows. Pathology: large cell anaplastic (LCA), classic (C), desmoplastic/nodular (D/N). Metastasis (M) status: positive (+), negative (−). Residual (R) disease status: >1.5 cm2 (+), <1.5 cm2 (−).