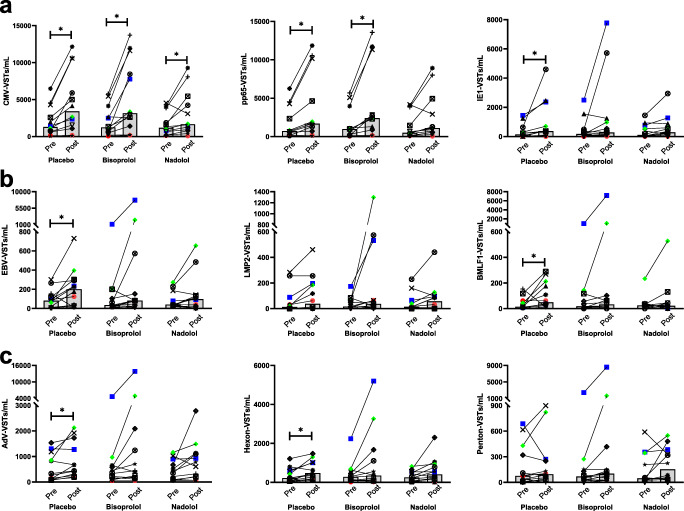
Fig. 2.
The frequency of virus-specific T cells in peripheral blood pre- and post-exercise. The number of circulating T cells specific for (a) CMV, (b) EBV, and (c) AdV was assessed in blood samples obtained from healthy participants after ingesting a placebo, a β1 AR antagonist (bisoprolol, 10 mg), or a β1 + 2 AR antagonist (nadolol, 80 mg) 3 h prior to exercise (pre) and immediately following 30 min of steady-state cycling exercise. The number of VSTs specific for each individual viral peptide were determined by IFN-γ ELISPOT, (a) the number of VSTs to CMV was determined by combining the number of VSTs to IE-1 and pp65, (b) the number of EBV-specific T cells was determined by combining the number of VSTs to LMP2 and BMLF1, and (c) the number of AdV-specific T cells was determined by combining the number of VSTs to hexon and penton. Bars represent the median value. n = 12 for all graphs excluding pp65 (n = 11). *Represents a significant (p < 0.05) Bonferroni-corrected p values comparing pre- with post-exercise. CMV = cytomegalovirus; EBV = Epstein-Barr virus; AdV = adenovirus