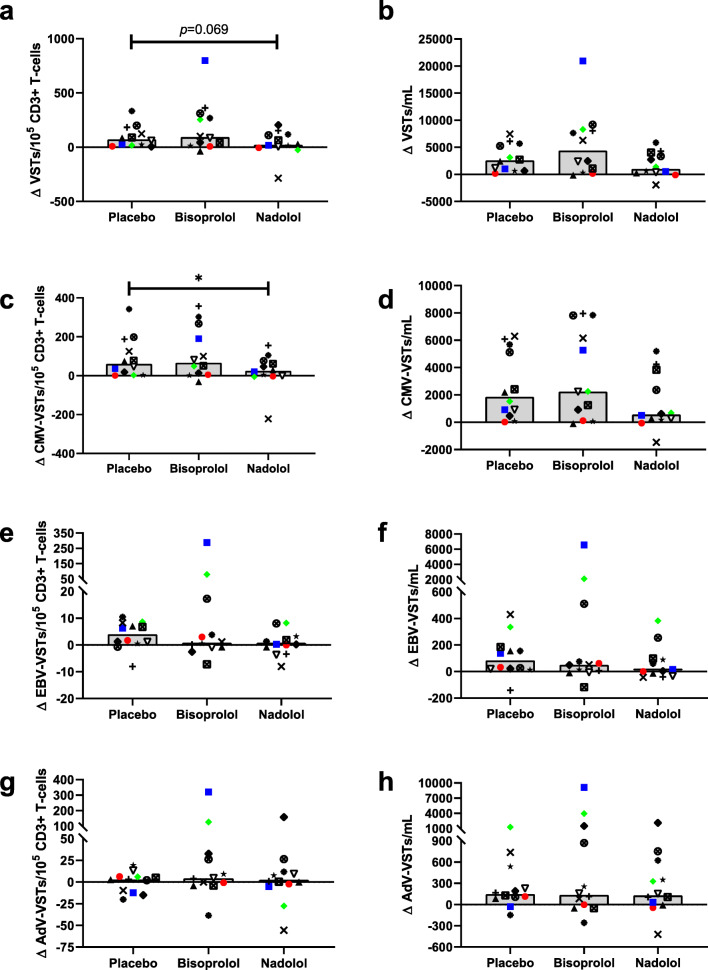
Fig. 3.
The effects of exercise and β AR blockade on the frequency and number of circulating VSTs. The absolute change from pre- to post-exercise in the frequency (per 100,000 CD3+ T cells) and number (per mL of whole blood) of VSTs in healthy participants (n = 12) after ingesting a placebo, a β1 AR antagonist (bisoprolol, 10 mg), or a β1 + 2 AR antagonist (nadolol, 80 mg) 3 h prior to exercise. Blood samples were obtained prior to medication ingestion and immediately following exercise. The number of VSTs specific for each virus was determined by IFN-γ ELISPOT. The change in the frequency of VSTs (left) and the number of circulating VSTs (right) for each drug trial are presented for (a, b) the total number of VSTs, determined by combining the number of VSTs to CMV, EBV, and AdV; (c, d) the number of VSTs to CMV, determined by combining the number of VSTs to IE-1 and pp65; (e, f) the number of EBV-specific T cells, determined by combining the number of VSTs to LMP2 and BMLF1 and (g, h) the number of AdV-specific T cells, determined by combining the number of VSTs to hexon and penton. Bars represent the median value. Bonferroni-corrected pair-wise comparison p values are presented. *Represents a significant (p < 0.05) pairwise difference between two conditions. VST = virus-specific T cell; CMV = cytomegalovirus; EBV = Epstein–Barr virus; AdV = adenovirus