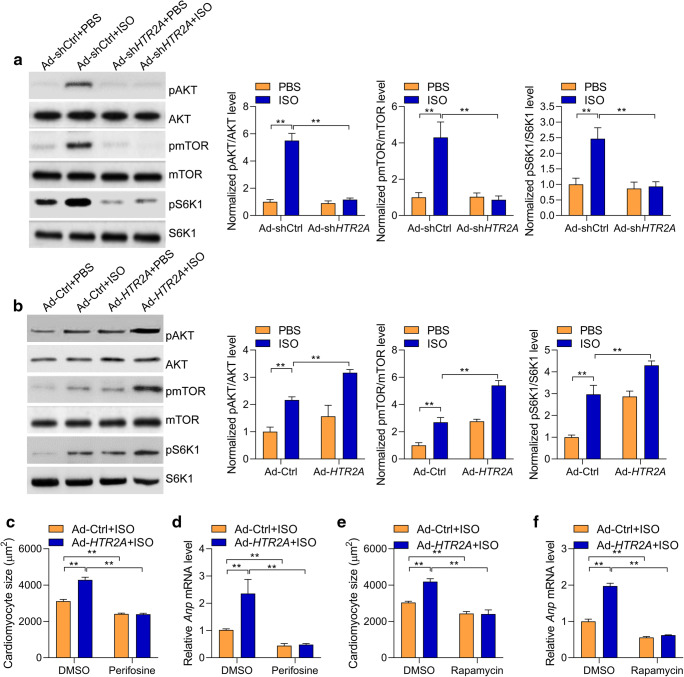
Fig. 3.
HTR2A promotes AKT-mTOR-S6K1 signaling activation. a HTR2A knockdown represses AKT-mTOR-S6K1 signaling activated by ISO in rat cardiomyocytes. Cardiomyocytes with/without HTR2A knockdown were subjected to ISO treatment (50 μM) for 24 h. mTOR, mammalian target of rapamycin; S6K1, p70 ribosomal protein S6 kinase 1. Representative western blot and quantitative results are shown (n = 3). b HTR2A overexpression promotes AKT-mTOR-S6K1 signaling activated by ISO in rat cardiomyocytes. Cardiomyocytes with/without HTR2A overexpression were subjected to ISO treatment (50 μM) for 24 h. Representative western blot and quantitative results are shown (n = 3). c, d Inhibition of AKT represses HTR2A function in cardiomyocyte hypertrophy. Rat cardiomyocytes with/without HTR2A overexpression were subjected to hypertrophy induction with ISO (50 μM) treatment for 48 h. The cardiomyocytes were also treated with/without AKT inhibitor perifosine (1 μM). Cardiomyocyte size was quantified with the ImageJ software (c), and the expression of hypertrophy-associated fetal genes was analyzed with qRT-PCR (d, n = 3 in each group). e, f Inhibition of mTOR represses HTR2A function in cardiomyocyte hypertrophy. Rat cardiomyocytes with/without HTR2A overexpression were subjected to hypertrophy induction with ISO (50 μM) treatment for 48 h. The cardiomyocytes were also treated with/without AKT inhibitor rapamycin (100 nM). Cardiomyocyte size was quantified with the ImageJ software (e), and the expression of hypertrophy-associated fetal genes was analyzed with qRT-PCR (f, n = 3 in each group). **P < 0.01 analyzed by two-way ANOVA followed by the Tukey post hoc test. Cardiomyocyte culture sets were performed on three different dates. Western blot was performed for each experiment set, and representative western blot results were shown