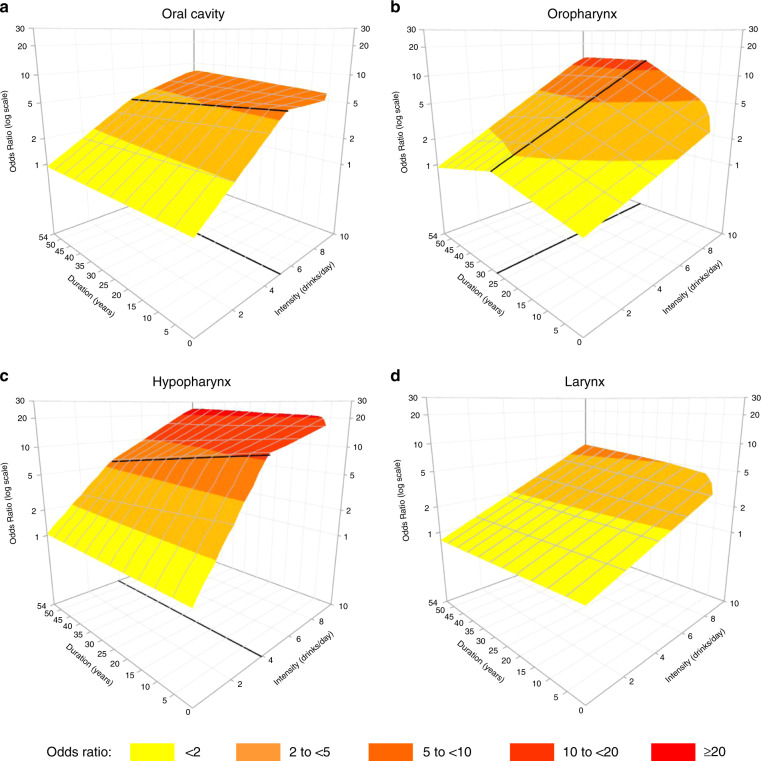
Fig. 1. Cancer risk for the joint exposure to drinking intensity and duration (3D representation).
Bivariate spline model’s estimates of odds ratios of oral cavity (a), oropharyngeal (b), hypopharyngeal (c), and laryngeal (d) cancers in current drinkers for the joint effect of intensity and duration of alcohol consumption. On the grid, black thicker lines represent knot locations, at 5 drinks/day for oral cavity, at 4 drinks/day for hypopharyngeal cancer and at 28 years for oropharyngeal cancer.