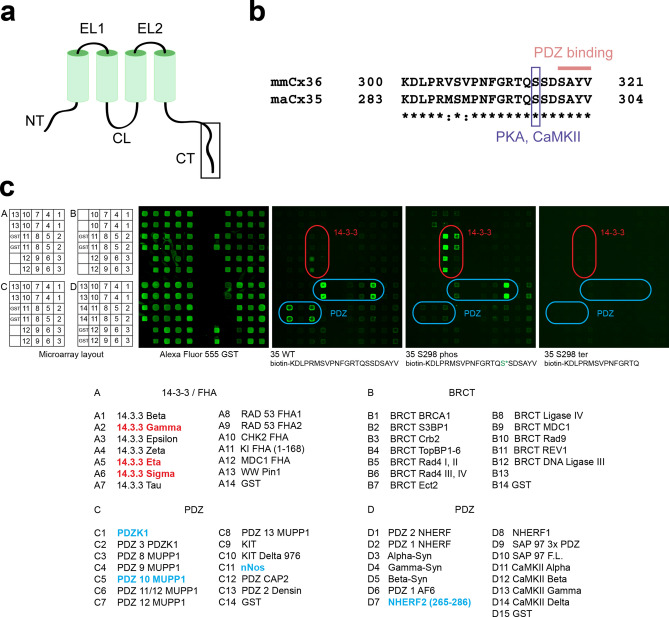
Figure 1.
Protein microarray data indicate that phosphorylation of S298 in maCx35 may act as a functional switch. (a) Membrane topology of connexins. N- and C-terminal tails (NT and CT, respectively) and the cytoplasmic loop (CL) reside inside the cytoplasm. The two extracellular loops (EL) are also indicated. (b) Sequence of the C-terminal end of maCx35/mmCx36, as indicated by the box in (a). Sequence identity (*) is high for mmCx36 and maCx35 at the C-terminal end. The blue box indicates a PKA/CaMKII consensus site at position S315 and S298 for mmCx36 and maCx35, respectively. The last four amino acids represent a PDZ binding domain, present in both proteins. (c) Microarray layout (A-D); the respective baits (all fused to GST) are found below. An array probed with Alexa Fluor 555 anti-GST antibody served as positive control. Peptides fused to biotin containing the C-terminal tail of maCx35 (35 WT), phosphorylated maCx35 (35 S298 phos), and a truncated version (35 S298 ter) were used as probes and showed differential results, marked by rounded squares. 14–3–3 proteins (red) and NHERF2 aa265-288 (blue D7) showed an increased binding to the 35 S298 phospho probe compared to 35 WT. In contrast, PDZK1, PDZ10 of MUPP1, and nNOS (blue) decreased their binding to the 35 S298 phospho probe. The truncated 35 S298 ter probe showed no binding interactions.