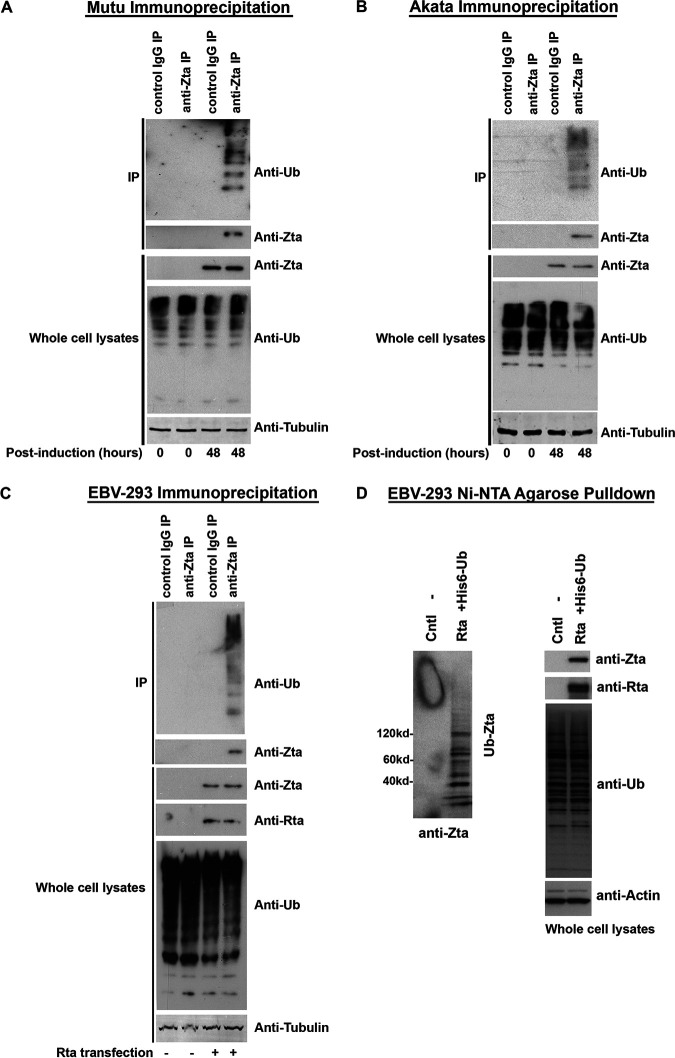
FIG 2.
Endogenously expressed Zta is ubiquitinated following activation of the lytic cycle in Mutu cells, Akata cells, and EBV-293 cells. (A) EBV lytic reactivation was induced in EBV-positive Mutu cells by anti-human IgM treatment. At 0 h and 48 h postinduction, cell extracts were prepared and immunoprecipitated with either a control IgG antibody or an anti-Zta antibody. Immunoprecipitates were analyzed for ubiquitin and Zta by Western blot analysis. The levels of Zta, ubiquitin, and α/β tubulin in the whole-cell lysates were also analyzed by Western blot analysis. (B) EBV lytic reactivation was induced in EBV-positive Akata cells by anti-human IgG treatment. At 0 h and 48 h postinduction, cell extracts were prepared and immunoprecipitated with either a control IgG antibody or an anti-Zta antibody. Immunoprecipitates were analyzed for ubiquitin and Zta by Western blot analysis. The levels of Zta, ubiquitin, and α/β tubulin in the whole-cell lysates were also analyzed by Western blot analysis. (C) EBV lytic reactivation was induced in EBV-293 cells by transfection of an EBV Rta expression vector. At 48 h postinduction, cell extracts were prepared and immunoprecipitated with either a control IgG antibody or an anti-Zta antibody. Immunoprecipitates were analyzed for ubiquitin and Zta by Western blot analysis. The levels of Zta, Rta, ubiquitin, and α/β tubulin in the whole-cell lysates were also analyzed by Western blot analysis. (D) EBV lytic reactivation was induced in EBV-293 cells by transfection of an EBV Rta expression vector. After 48 h, cells were lysed under denaturing conditions and extracts were purified over nickel-NTA beads. The purified material was assayed by Western blot analysis employing an anti-Zta antibody. Expression levels of Zta, Rta, ubiquitin, and actin were determined by Western blot analysis of whole-cell lysates.