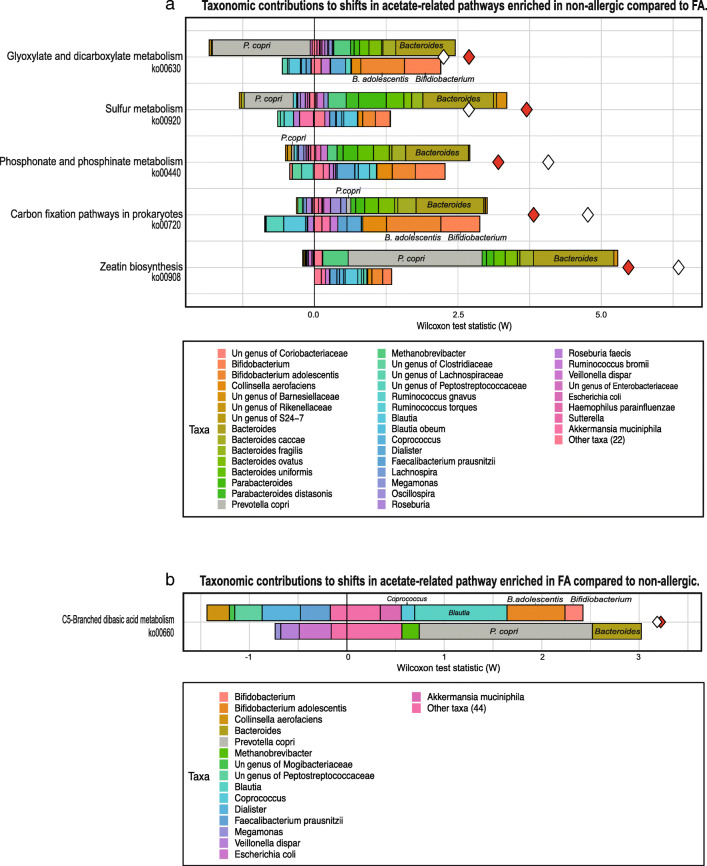
Fig. 7.
Acetate pathways differ between allergic and non-allergic individuals. a Taxonomic contributors of differentially abundant acetate-related KEGG pathways, as quantified by FishTaco (only those with FDR < 0.05 are shown). The taxonomic contributors are separated into taxa that are over-represented in the group the pathways are enriched in and contribute positively to the observed shift in cases (upper right bars), taxa that are over-represented in the group the pathways are depleted in and contribute positively to the observed shift in cases (lower right bars), and taxa that are attenuating the observed shift (left bars). Taxa contributing to the observed over-representation of acetate-related KEGG pathways in the non-allergic group compared to the FA group. b Taxa contributing to the observed over-representation of an acetate-related KEGG pathway in the FA group compared to the non-allergic group. The red diamonds represent the Wilcoxon rank-sum statistic (W statistic) for the difference in pathway abundances between groups inferred from KO profiles, and the white diamond represents the W statistic when comparing pathway abundances between groups inferred from taxonomic profiles and genomic content. Un, unclassified