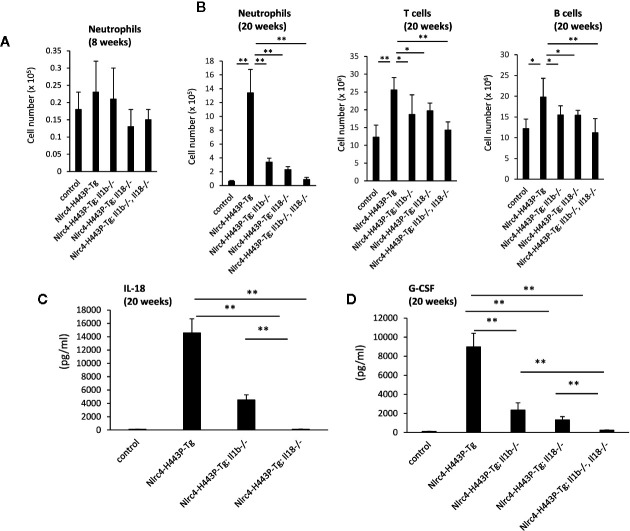
Figure 1.
IL-1β– and Il-18–mediated inflammation in Nlrc4-H443P-Tg mice. (A) Total neutrophil numbers in the spleens of control, Nlrc4-H443P-Tg, Nlrc4-H443P-Tg/Il1b−/−, Nlrc4-H443P-Tg/Il18−/−, and Nlrc4-H443P-Tg/Il1b−/−Il18−/− mice at the age of 8 and weeks were determined (N = 8 in each group). The neutrophils were defined as CD11b+Gr-1high cells. The data are shown as the mean ± SD. *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01. (B) Total neutrophil, T cells or B cells numbers in the spleens of control, Nlrc4-H443P-Tg, Nlrc4-H443P-Tg/Il1b−/−, Nlrc4-H443P-Tg/Il18−/−, and Nlrc4-H443P-Tg/Il1b−/−Il18−/− mice at the age of 20 weeks were determined (N = 8 in each group). The data are shown as the mean ± SD. *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01. Serum (C) IL-18 was measured in control, Nlrc4-H443P-Tg, Nlrc4-H443P-Tg/Il1b−/− and Nlrc4-H443P-Tg/Il18−/− mice at the age of 20 weeks (N = 5 in each group), and serum (D) G-CSF was measured in control, Nlrc4-H443P-Tg, Nlrc4-H443P-Tg/Il1b−/−, Nlrc4-H443P-Tg/Il18−/−, and Nlrc4-H443P-Tg/Il1b−/−Il18−/− mice at the age of 20 weeks (N = 5 in each group). Data are shown as the mean ± SD. **P < 0.01.