Fig. 1.
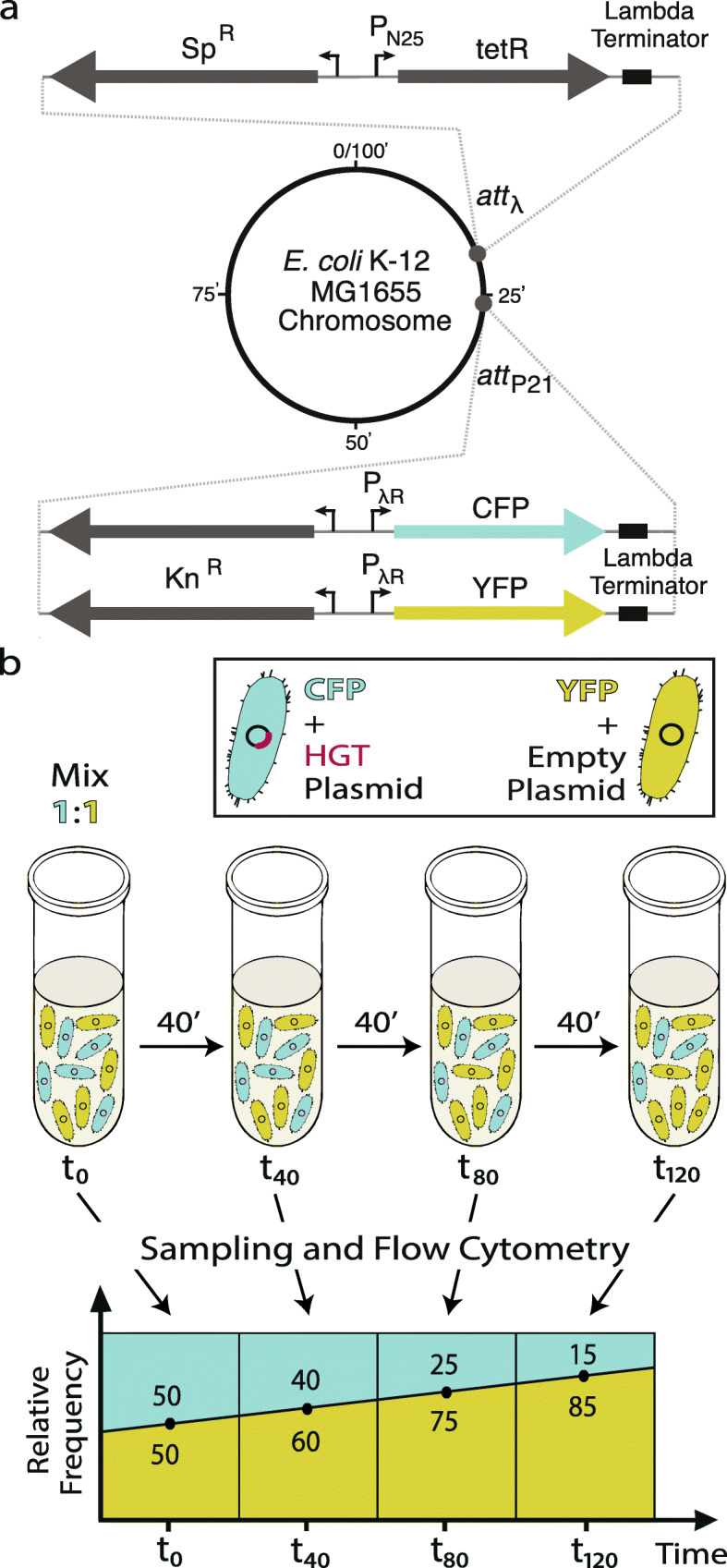
Schematic representation of the experimental design. a. Chromosomal modifications in the recipient strain, E. coli MG1655 att-λ::(tetR-SpR) att-p21::(CFP/YFP-KnR), for the transferred genes. Att-λ and att-p21correspond to the attachment sites of the phage λ and p21, respectively. TetR is the repressor protein controlling the expression of the transferred genes. SpR and KnR are the resistance genes for spectinomycin and kanamycin, respectively. PN25 and PλR are the constitutive promoters. See Methods section for details. b. Depiction of the competition assay. Blue cells with CFP represent the ‘mutant’ strain that carries the pZS*-HGT plasmid containing the introduced gene, whereas yellow cells with YFP represent the ‘wild type’ strain that carries the empty pZS*-HGT plasmid without the introduced gene. The plot illustrates an example where the fitness effect of the gene is deleterious, resulting in a decrease in the frequency of blue cells over time. Numbers inside the segments represents the frequency of the type of the cell with same color
