Figure 1.
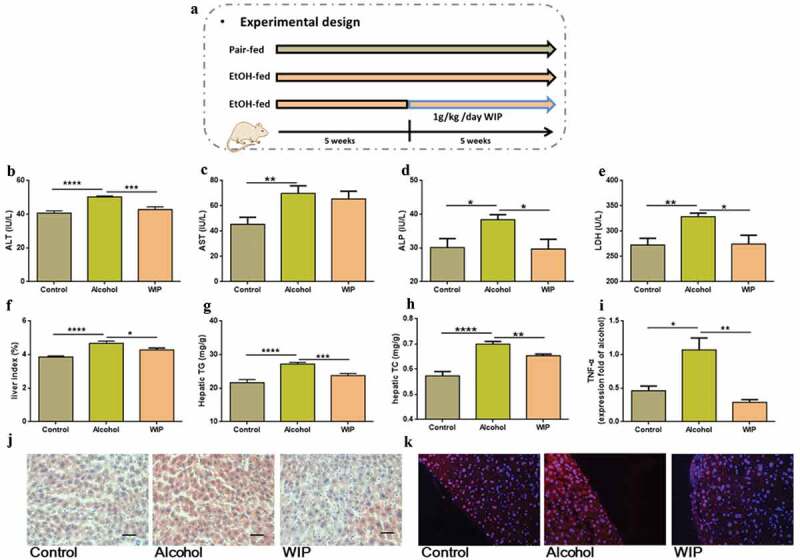
Oral treatment with WIP alleviates chronic ethanol feeding-induced hepatic injury and steatosis
(a) Experimental design. (b) The level of plasma alanine aminotransferase (ALT). (c) The level of plasma aspartate aminotransferase (AST). (d) The plasma levels of alkaline phosphatase (ALP). (e) The level of plasma lactate dehydrogenase (LDH). (f) Liver index. (g) The level of hepatic triglyceride (TG). (h) The level of hepatic total cholesterol (TC). (i) The expression of TNF-α in liver. (j) Representative picture of liver sections stained with oil-red. (k) Representative picture of liver sections with MCP-1 immunofluorescence staining. (b-h) N = 10 per group, (i) N = 5 per group, (j-k) N = 3 per group. Control: mice received isocaloric liquid diet instead of ethanol. Alcohol: mice fed with ethanol diet. WIP: mice fed with an ethanol diet supplemented with a water-insoluble polysaccharide from W. cocos. Data are presented as the mean ± standard error of the mean (SEM). Statistical analysis was done using one-way ANOVA followed by the Tukey post hoc test. Compare to Alcohol: * P < .05; ** P < .01; *** P < .001; **** P < .0001.
