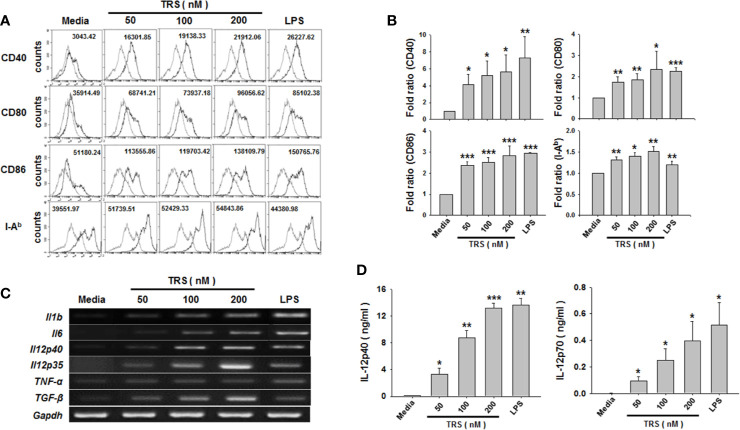
Figure 1.
Threonyl-tRNA synthetase (TRS) increases the expression levels of surface molecules and cytokines in bone marrow-derived dendritic cells (DCs). Bone marrow-derived DCs were isolated from C57BL/6 mice as described in the Materials and Methods. Immature-DCs (iDCs) were cultured for 20 h (A, D), or 6 h (C) with threonyl-tRNA synthetase (TRS; 50, 100, and 200 nM) or lipopolysaccharide (500 ng/ml). (A) The expression of CD40, CD80, CD86, and I-Ab molecules, as detected by flow cytometry for CD11c+ gated cells. Gray histograms, isotype control; black histograms, anti-CD40, anti-CD80, anti-CD86, and anti-I-Ab Ab. Representative figures are presented. The value shown in the histograms represents the mean fluorescence intensity. (B) The fold ratio of surface molecules expression was plotted with the media-treated DCs as 1.0. The data represent mean ± SD of three independent experiments (n = 3); *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01 and ***P < 0.001 compared with media-treated DCs. (C) mRNA levels of pro-inflammatory cytokines, as confirmed by reverse transcriptase-polymerase chain reaction. GAPDH is used as a control. (D) Levels of IL-12p40 and IL-12p70 in cell supernatants, as detected by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. Experiments were conducted three times independently and are represented as the mean ± SEM of results performed in triplicate (n = 3). Statistical significance was assessed using unpaired Student’s t-test; *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01 and ***P < 0.001 compared with media-treated DCs.