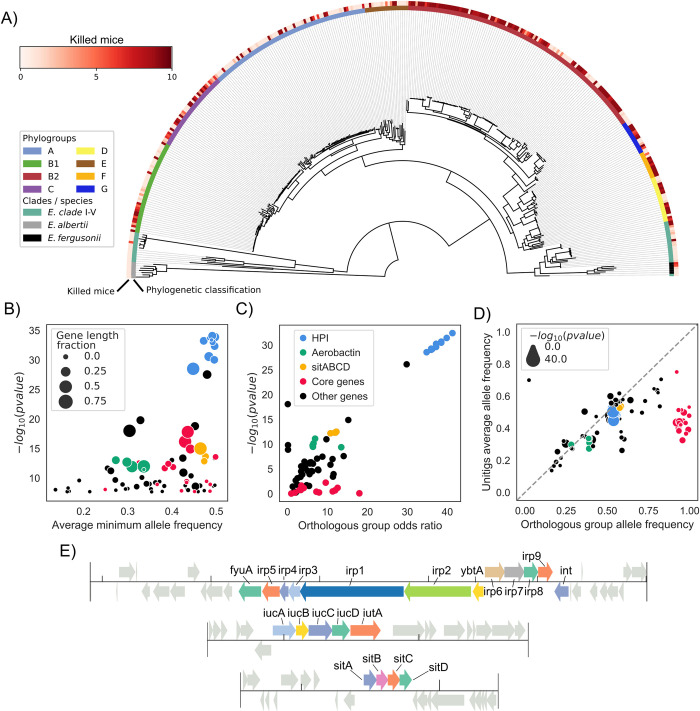
Fig 1. The HPI is strongly associated with the extra-intestinal virulence phenotype assessed in the mouse sepsis assay.
A) Core genome phylogenetic tree of the Escherichia strains used in this study rooted on E. albertii strains. Outer ring reports virulence as the number of killed mice over the 10 inoculated per strain, inner ring the phylogroup, clade or species each strain belongs to. B) Results of the unitigs association analysis: for each gene the minimum association p-value and average minimum allele frequency (MAF) across all mapped unitigs is reported. The gene length fraction is computed by dividing the total length of mapped unitigs by the length of the gene. The color of each gene follows the same key as panel C. C) Results of the gene presence/absence association analysis; only those genes with at least one associated unitig mapped to them are represented. D) Scatterplot of gene frequency versus frequency of associated unitigs; points on the diagonal indicate hits where the association is most likely due to a gene’s presence/absence pattern rather than a SNP. The color of each gene follows the same key as panel C. E) The structure of the HPI and of the aerobactin and sitABCD operons in strain IAI39; all associated genes are highlighted.