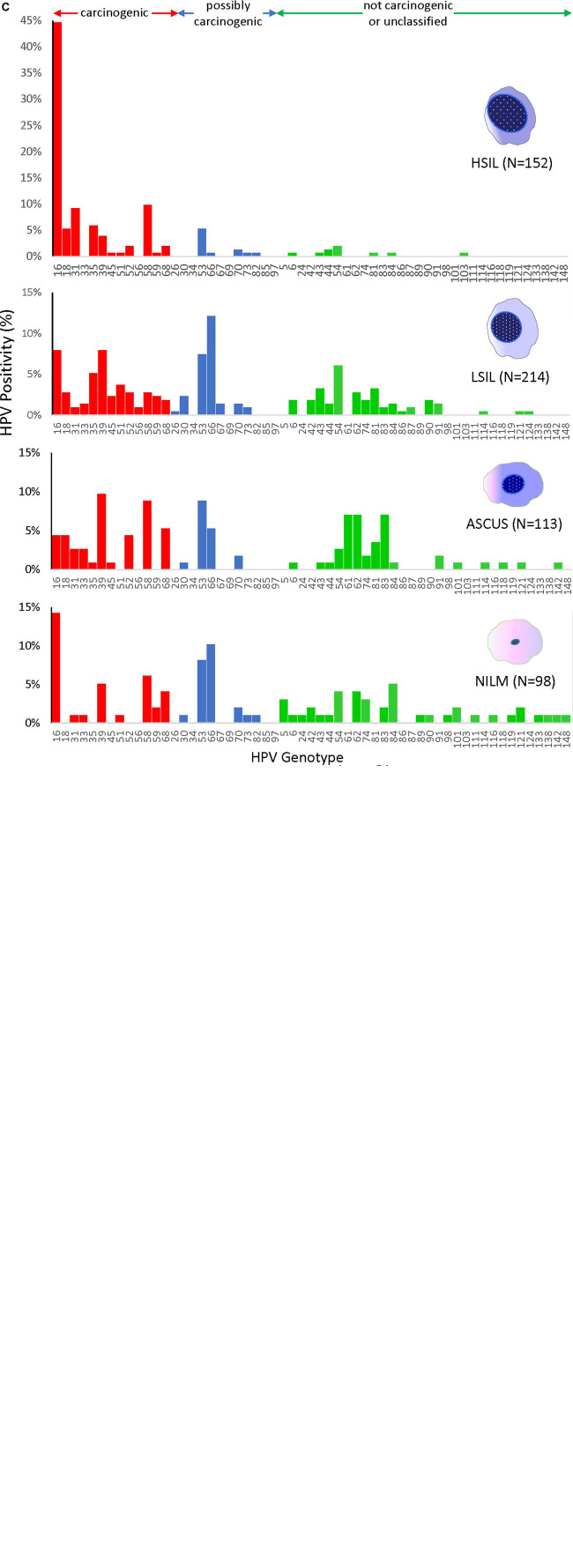
FIGURE 2.
HPV prevalence and genotype distribution found in 4 cytological grades. (A) HPV DNA positivity rate for 883 samples as determined by PCR amplification and gel electrophoresis. The positive rates for NILM and ASCUS were over 50%, whereas the rates were significantly higher for LSIL and HSIL at ∼80–90% (top) (*p < 0.05, chi-square test). (B) Distribution of HPV-positive rates stratified by type-specific carcinogenic potential for PCR-positive/sequenced samples (n = 640). Progression of cytological grade from NILM to HSIL correlated with a significant uptrend in carcinogenic HPV-types and a downtrend in possibly and not carcinogenic/unclassified HPV-types (*p < 0.05, chi-square trend test). Samples with poor or noisy sequence quality unidentifiable by BLAST also decreased with worsening cytological grade (*p < 0.05, chi-square trend test). (C) HPV genotype distribution of 577 cytology samples as determined by PCR/Sanger sequencing according to cytological diagnoses. The remaining 63 HPV-positive samples could not be genotyped due to poor sequence quality and/or overlapping sequences of mixed infections. The proportion of carcinogenic HPV genotypes (red bars) increased coincidently with cytological grade (*p < 0.05, chi-square trend test). In contrast, the possibly and not carcinogenic/unclassified HPV-types (blue and green bars, respectively) significantly diminished (*p < 0.05, chi-square trend test). Simultaneously, species richness diminished from NILM to HSIL (38 to 23 genotypes, respectively) while HPV-16 surged in 68/152 (45%) HSIL samples. ASC-US, atypical squamous cells of undetermined significance; CARC, carcinogenic HPV; HSIL, high- grade squamous intraepithelial lesion; LSIL, low-grade squamous intraepithelial lesion; NA, not available/identifiable by BLAST; NILM, negative for intraepithelial lesion or malignancy; NOT CARC, not carcinogenic; NS, not significant; POSS CARC, possibly carcinogenic Stars, p < 0.01.