TABLE 1.
Studies on controlling biofilm by targeting QS signaling molecule.
| Source | QS-inhibiting agents | Chemical structure | Target bacteria | Effects | References |
| Bacillus cereus VT96 | AHL-lactonase AiiA | NA |
P. aeruginosa V. cholerae E. cloacae |
Degraded AHLs, prevent the biofilm formation and production of virulence factors | Augustine et al., 2010; dos Reis Ponce et al., 2012; Anandan and Vittal, 2019 |
| Synthesis | Molecularly imprinted polymers (MIPs) | 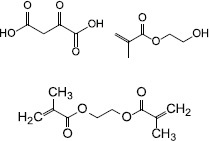 |
P. aeruginosa | Captured OdDHL, therefor interrupted QS, and subsequently inhibit biofilm formation | Ma et al., 2018 |
| Arthrobacter nitroguajacolicus strain Rü61a | 3-Hydroxy-2-methyl-4(1H)-quinolone 2,4-dioxygenase Hod | NA | P. aeruginosa | Catalyzed the conversion of PQS to N-octanoylanthranilic acid and carbon monoxide, reduced the expression of the PQS-regulated virulence | Pustelny et al., 2009 |
| Derivative | Boronic acid derivate SM23 | NA | P. aeruginosa | Decreased 3-oxo-C12-HSL and C4-HSL and reduced biofilm formation | Peppoloni et al., 2020 |
| Synthesis | Acyl-HSL analog J8-C8 | 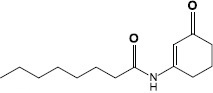 |
B. gluma | Bound to TofI, disturbed C8-HSL synthesis, affected biofilm formation | Chung et al., 2011 |
| Synthesis | Diketopiperazines | 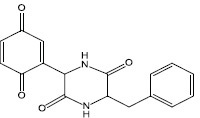 |
B. cenocepacia | Interfered with the activity of signal molecule synthase CepI and rendered the bacteria unable to produce biofilm | Buroni et al., 2018 |
| Synthesis | Anti-autoinducer monoclonal antibody AP4-24H11 | NA | S. aureus RN4850 | Sequestrated the autoinducing peptide (AIP)-4, inhibited QS and biofilm formation | Park et al., 2007 |
| Gene from a soil metagenome | NADP-dependent reductase BpiB09 | NA | P. aeruginosa PAO1 | Reduced pyocyanin production, decreased motility, poor biofilm formation | Bijtenhoorn et al., 2011 |
| Synthesis | 3-(dibromomethylene) isobenzofuran-1(3H)-one derivatives | 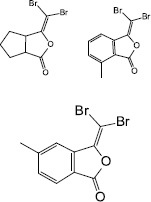 |
F. nucleatum P.gingivalis T. forsythia |
Inhibited biofilm formation through the inhibition of AI- 2 activity | Park et al., 2017 |
NA, not available.
