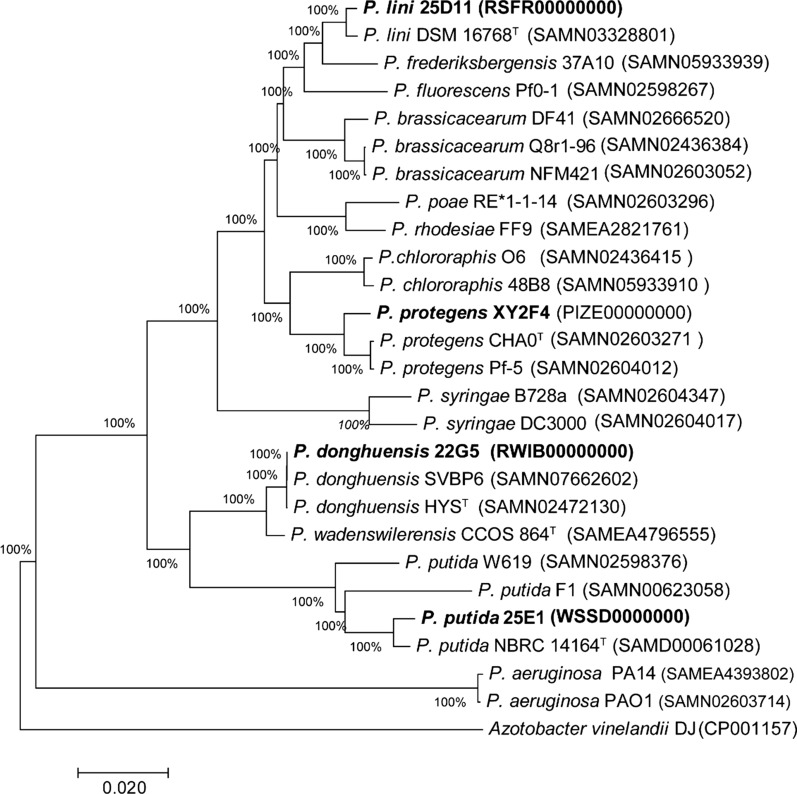
Fig. 2.
Phylogenetic tree depicting the evolutionary relationships of Pseudomonas spp. Genomes of previously reported strains were downloaded from The Pseudomonas Genome Database (https://www.pseudomonas.com/). The annotation was performed using RAST (Overbeek et al. 2014). The phylogenetic tree was generated with MEGA software using concatenated sequences of 10 housekeeping genes (acsA, aroE, dnaE, guaA, gyrB, mutL, ppsA, pyrC, recA, and rpoB) (Loper et al. 2012). Strains in this study are indicated with a star (*). Type strains or representative strains of multiple documented Pseudomonas species were compiled to build the tree. Azotobacter vinelandii DJ was used as the outgroup